Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
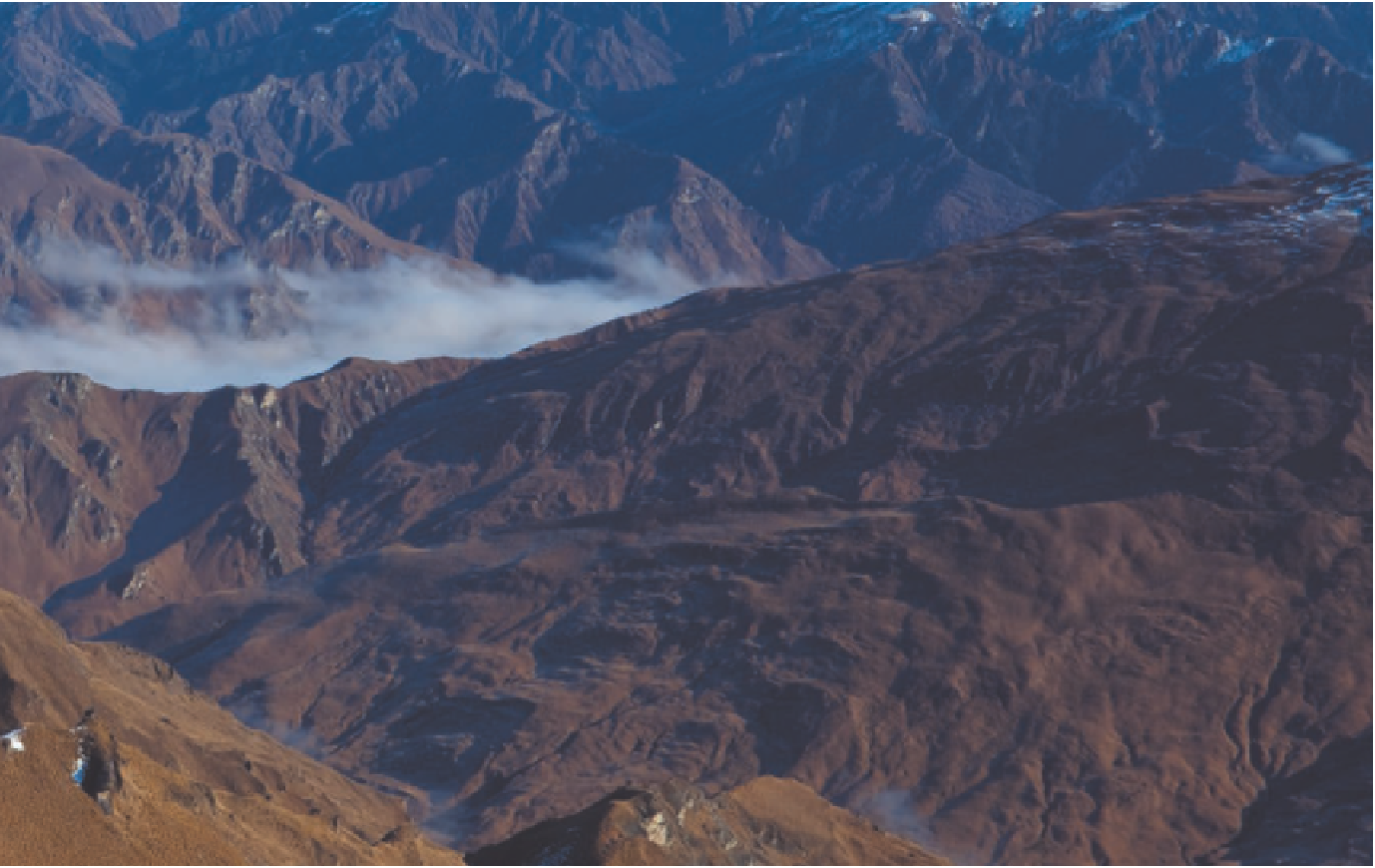
© Doug Pearson/JAI/Corbis
Mountainous landscapes are some of the most spectacular on Earth, as this image from the Southern Alps of New Zealand clearly
shows. Mountains such as these pictured here form by tectonic processes, which consist of movements within the Earth's crust
that deform rocks, build volcanoes, and cause earthquakes. This chapter focuses on those processes and the landforms that result.
L E A R N I N G O B J E C T I V E S
C H A P T E R P R E V I E W
1.
Describe the theory of plate tectonics and the
evidence supporting the concept of continental drift.
2.
Explain the various types of plate movements that
occur as a result of continental drift.
3.
Discuss how plate convergence promotes folding of
rock, resulting in the formation of anticlines, synclines,
and other structural features.
4.
Explain the general development of the Appalachian Moun-
tains and why segments of the Ridge and Valley Province
may be structurally more complex than they appear.
5.
Compare and contrast the various kinds of faults that
occur on Earth.
6.
Describe why earthquakes occur, the various features
associated with them, and how their location can be
precisely determined.
7.
Compare and contrast the various types of volcanoes
and why they occur.
8.
Discuss the Pacific Ring of Fire and explain the
geography of the Cascade Volcanic Arc.
Plate Tectonics
Continental Drift
Types of Plate Movements
Folding
Plate Tectonics
Earthquakes
Human Interactions: Earthquakes as
Natural Hazards
Types of Faults
Volcanoes
Walk the Pacific Ring of Fire
Volcanoes