Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Figure 11.14 Soil texture.
Soils
form in parent material that con-
tains particles ranging in size from
sand to clay.
0.001 mm
0.002 mm
0.05 mm
2.0 mm
Colloids
Clay
Silt
Sand
Gravel
0.00004 in.
0.00008 in.
0.002 in.
0.08 in.
from pure black (0/) to pure white (10/).
Chroma
is the relative
strength of the spectral color. The scales of chroma for soils
extend from /0 for neutral colors to a chroma of /8 for the stron-
gest soil color. To put it all together, a soil that is pale brown,
for example, is designated 10YR 6/3. In contrast, a soil that is
very dark brown has a Munsell designation of 10YR 2/2. Still
another example is a soil that has a yellowish red (7.5YR) hue
and is strong brown in color. This soil would have a 7.5YR 5/6
color designation.
2.
Texture
As discussed earlier, soil contains a multitude
of inorganic particles that are typically related to the
parent material. Most soils contain a continuum of three
distinct size categories (Figure 11.14), which are (in order
from largest to smallest) sand, silt, and clay. Some larger
(gravel) and smaller (colloid) particles may also be pres-
ent. The combined percentages of these soil particulates
are referred to as the textural class of the soil, as shown in
the soil textural triangle in Figure 11.15.
100
10
90
80
20
30
70
Clay
60
40
Percent
clay
Percent
silt
50
50
Silty
clay
Example 1
Sandy
clay
40
60
Clay loam
Silty clay
loam
30
70
Sandy clay
loam
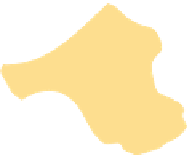
Figure 11.15 Soil textural triangle.
Soils
can be texturally classified based on the
relative proportion of sand, silt, and clay
in the parent material. For percent sand,
use the lines slanting from the bottom of
the triangle up to the left; for percent silt,
use the lines slanting from the right side
of the triangle down to the left; for percent
clay, use the horizontal lines. Examples 1
and 2 described in the text are shown.
20
80
Loam
Example 2
Silt loam
10
Sandy loam
90
Loamy
sand
Silt
Sand
100
Percent sand