Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
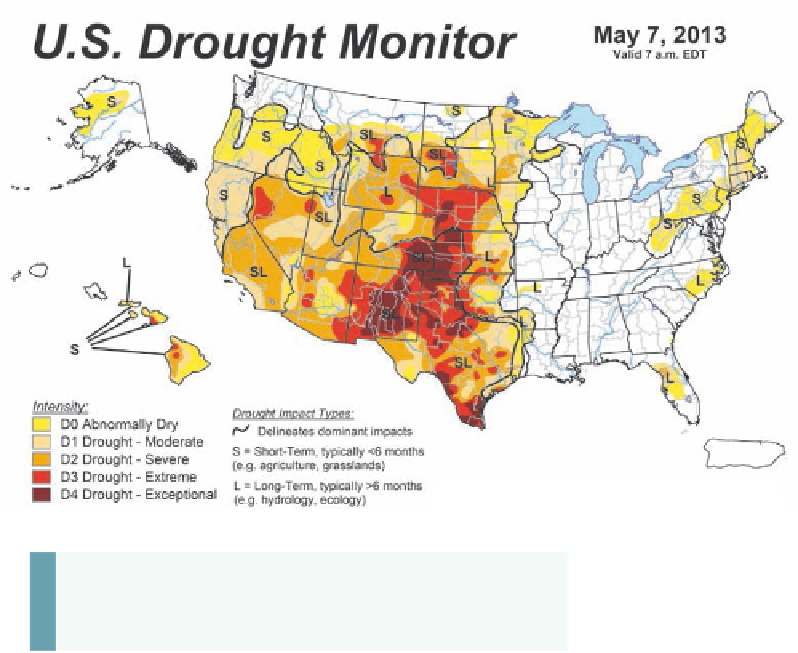
figure 7.29 u.S. Drought
monitor on may 7, 2013.
When compared to the
map in Figure 7.28b, note
that the drought had eased
considerably in the eastern
part of the affected area.
On the other hand, this
map shows intensifica-
tion of the drought in the
central and southwestern
Great Plains.
KEY CONCEPTS TO REMEMBER ABOUT
PRECIPITATION AND PRECIPITATION
PROCESSES
4.
Convectional uplift occurs when a bubble of air rises due
to unequal heating of the Earth's surface. The bubble of
air continues to rise as long as the air is unstable, that
is, as long as the temperature of the bubble is warmer
than the surrounding air. When these temperatures be-
come equal, the air is stable.
1.
In order for precipitation to occur, condensation nuclei
must be present in the form of dust particles or other
small solids.
5.
Orographic uplift refers to the rising air that occurs due
to a blocking mountain range. The windward side of the
range faces the oncoming winds, whereas the leeward
side is the downwind side. Condensation occurs on the
windward side; the leeward side is typically in the rain
shadow and is dry.
2.
Water droplets remain in suspension as clouds until they
grow sufficiently large to fall under the force of gravity.
3.
For precipitation to occur, some mechanism must be
present to cause sufficient uplift of an air parcel such
that high amounts of condensation take place.
S u m m a r y o f K e y C o n C e p t S
1.
Water molecules are attracted to one another through
hydrogen bonding. Given the unique nature of this bond,
water can exist in three physical states: liquid (water),
solid (ice), and gas (water vapor).
vapor a parcel of air can hold. This variable depends on
temperature, with warm air having a higher maximum hu-
midity than colder air. Specific humidity measures how
much water vapor is in the air. Relative humidity is the ra-
tio of specific humidity to maximum humidity. The dew-
point temperature is the temperature at which a mass of
air becomes saturated. This is the temperature at which
condensation occurs in that air mass. As specific humid-
ity increases, so does dew-point temperature.
2.
Latent heat is stored in water molecules. When water
changes phase, latent heat is either absorbed or re-
leased, depending on the transformation.
3.
The hydrologic cycle refers to the ways in which wa-
ter moves on Earth through the combined processes
of evaporation, precipitation, and runoff. Most water is
stored in the oceans, which are a net source of evapora-
tion in the context of the global water balance. On land-
masses, more precipitation occurs than evaporation.
5.
Adiabatic processes refer to the temperature changes
that occur in an air parcel due solely to changes in air
pressure. When air pressure increases, a parcel of air is
compressed and warms adiabatically. In contrast, when
air pressure decreases, a parcel of air expands and thus
cools internally because air molecules are spaced far-
ther apart. Air cools at the dry adiabatic lapse rate (DAR)
4.
Three kinds of humidity occur: maximum, specific, and
relative. Maximum humidity refers to how much water