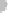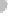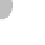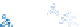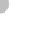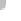Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
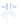
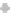
Condensation
nuclei (dust, etc.)
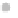
Condensation
nuclei (dust, etc.)
Small liquid drops,
ice crystals form
Small liquid
drops form
Ice crystals grow
larger, absorb
liquid drops
Liquid drops
coalesce into
larger drops
Snowflakes form
Raindrops form
(a)
(b)
Figure 7.20 Types of precipitation.
(a) Snowflakes form by the crystallization of ice particles. (b) Raindrops form through
coalescence of small water droplets.
This kind of air lifting takes place in one of four ways
(Figure 7.21). One way that air rises is through the process of
convectional uplift
, which results in distinct bubbles of air
rising through denser surrounding air. Another way is called
orographic uplift
, which occurs when air is forced to flow up
and over mountains. A third way is through the collision of
large air masses along frontal boundaries. This process is called
frontal uplift
and typically occurs when contrasting bodies of
air collide. The fourth way in which large parcels of air can
uplift is through the process of
convergent uplift
. Convergent
uplift occurs whenever bodies of air meet at a central location,
forcing air upward at that point. Although this process is some-
times associated with low-pressure systems, it is most com-
mon in the low latitudes along the Intertropical Convergence
Zone (ITCZ), where air from the Northern and Southern Hemi-
spheres converges.
The remainder of this chapter focuses on convectional and
orographic processes because they are relatively limited in a
geographic extent and beautifully exemplify adiabatic processes
in a way that is easy to understand. Frontal and cyclonic pre-
cipitation processes are more complex because they are associ-
ated with major weather systems that influence entire regions
of the country in many different ways. These larger systems are
discussed in Chapter 8.
Orographic Uplift
A good place to begin a holistic dis-
cussion of rising air, adiabatic processes, and precipitation
is with the concept of orographic uplift because it makes so
Convectional uplift
Uplift of air that occurs when bubbles of
warm air rise within an unstable body of air.
Frontal uplift
Uplift of air that occurs along the boundary of
contrasting bodies of air.
Orographic uplift
Uplift that occurs when a flowing body of
air encounters a mountain range.
Convergent uplift
Uplift of air that occurs when large bodies
of air meet in a central location.