Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
VISUAL CONCEPT CHECK
4.3
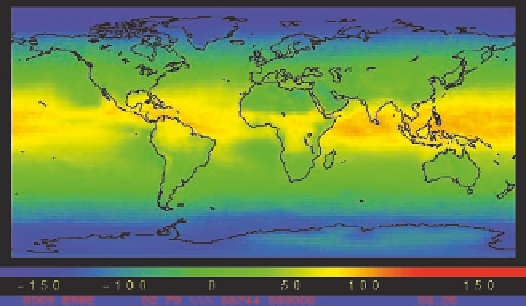
Net radiation refers to the total amount
of solar radiation received by Earth at any
given place and time. This image shows the
geography of mean net radiation during a
particular time of year, with yellows and red-
dish hues representing high values in watts
per square meter. Darker colors, in contrast,
represent low values of net radiation. By
observing this diagram, can you determine
what time of year it must be? What must
the Earth-Sun geometric relationship be like
during this time of year?
KEY CONCEPTS TO REMEMBER ABOUT
THE GLOBAL RADIATION BUDGET
is important because it drives atmospheric circulatory
processes.
4.
Net radiation depends on a complex interaction of sev-
eral variables, including angle of incidence, latitude,
season, day length, and albedo.
1.
The global radiation budget refers to the balance be-
tween incoming and outgoing radiation on Earth.
2.
Over the long term, the global radiation budget is bal-
anced. However, even though the long-term radiation
budget is balanced, a great deal of variability occurs
across Earth as a whole.
5.
In an effort to supplement current energy supplies, ef-
forts are under way to increase the production of re-
newable solar energy. The major limitations are that
production of solar energy with current technology is
inefficient and the Sun does not shine consistently in
many places.
3.
In general, low latitudes have a net surplus of radiation,
whereas high latitudes have a net deficit. This imbalance
s U m m A R y O F K E y C O n C E P T s
1.
The atmosphere serves as a protective shield that fil-
ters the potentially deadly effects of ultraviolet radiation
from the Sun, allowing mostly visible and infrared wave-
lengths to reach Earth.
4.
Albedo refers to the reflectivity of surfaces on Earth.
Snowy surfaces have the highest albedo, whereas dark-
er surfaces such as roads and oceans have the lowest
albedo. Overall, the Earth reflects about 31% of all in-
coming solar radiation through albedo.
2.
The lower part of the atmosphere is warmed primarily
due to the greenhouse effect. This warming occurs be-
cause variable gases in the atmosphere, such as carbon
dioxide and water vapor (as well as others), trap long-
wave radiation that is emitted by Earth.
5.
The global radiation budget refers to the overall balance
of incoming versus outgoing radiation. Earth receives
shortwave radiation from the Sun. This radiation is ei-
ther absorbed by the atmosphere and the various Earth
surfaces, or reflected and scattered back to the surface
or back into space. The radiation that reaches Earth's
surface is absorbed and then re-radiated as longwave
radiation. The overall radiation budget must be in bal-
ance; otherwise, Earth would become progressively hot-
ter or colder.
3.
Insolation refers to the amount of solar radiation received at
the top of the atmosphere. From this point, radiation follows
several paths. Approximately 50% of all radiation reaches
Earth, with some arriving directly and some indirectly. The
remaining radiation is either absorbed in the atmosphere,
scattered by dust, or reflected directly back into space.