Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
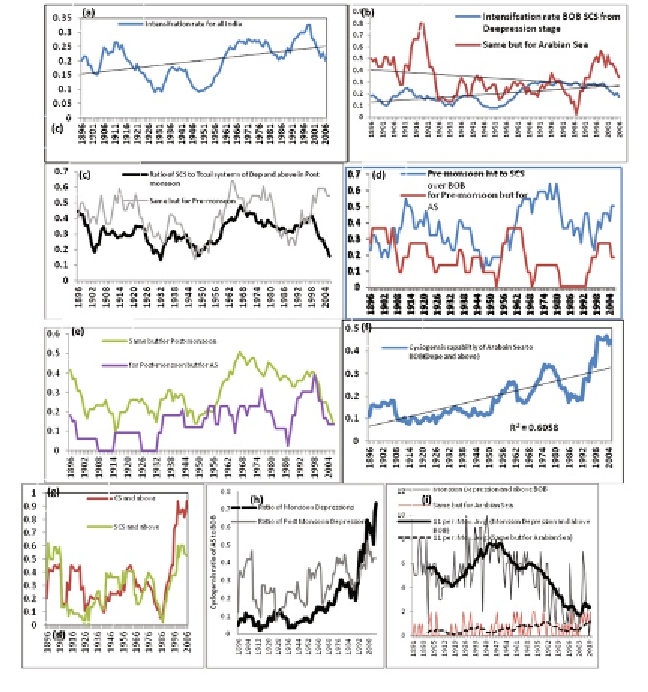
Fig. 4 (a-e):
Intensification ratio of cyclonic system over Indian region, AS and BoB
computed as ratio of total SCS intensified in a year or a season to total number of
yearly systems of depressions and above: (a-b) annual ratio for Indian region, AS and
BoB, (c) for cyclone season of pre-monsoon and post-monsoon for Indian region, (d-e)
same as (c) but for AS and BoB. (f-i): Cyclogenesis ratio of AS to BoB: (f) from ratio
of total annual systems formed in respective seas of Dep (D) and above, (g) from ratio
of annual frequencies of CS and above, SCS and above formed in respective seas, (h)
in two main seasons of monsoon and post-monsoon in respective seas of Dep and
above and (i) from actual frequencies of Dep and above during monsoon season where
highest trend over BoB vis-à-vis AS.
capability comparison using their actual frequencies during monsoon season
for AS and BoB. Figure 4f shows cyclogenesis ratio of AS to BoB as climatic
stable to 0.1-0.2 for a very long period of 1891-1970 i.e. with only 10-20% of
BoB's total number of annual cyclonic systems of D and above in a year formed
over AS. Thereafter, it has increased to 0.32 to 0.35 (i.e. about 35%) in mid
1970s for a small period of about a decade followed by decreasing back to
0.18 (i.e.18%) in mid 1980s. AS then remained cyclogenesis-wise very weak
Search WWH ::

Custom Search