Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
disrupting the flow of air, but as generating it. Using such a model as a basis is
possible; however, caution is required so that it becomes possible to be able to
distinguish between a type of wind, which is referred to as a synoptic wind (on a
general level), and a thermal breeze. Thermal breezes account for 80% of the winds
that occur in sheltered from main synoptic fluxes Mediterranean areas, such as the
in the region of Nice, France.
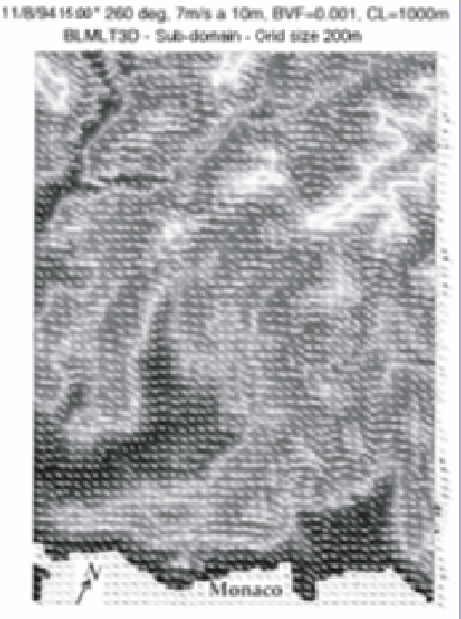
11/8/94, 50.00 * 260 deg, 7 m/s a 10 m, BVF=0.001,
CL= 1,000 m, BLMLT3D - sub-domain - grid size 200 m
Figure 8.1.
Example of a wind field recreated for the extreme Southeast of France
by a non-linear, hydrostatic model (BLMLT3D). The different shades of grey
correspond to different altitude levels. The grid is 200 m wide [CAR 94]
As far as the climatic variables are considered, physical logic can be used to
provide real-time information or to forecast. Physical logic is used as the basis of all
weather forecasts, and is used very effectively for short-term and medium-term
forecasts. Beyond a period of 8-15 days, the reliability of the forecasts decreases
due to reasons explained by chaos theory (due to problems associated with
initialization values and with the non-linearity of equations). Plotting a map with
just the average values (and not a given moment) assumes that each average value
has been calculated from every individual situations that have occurred, so that the
determinist logic is respected.