Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
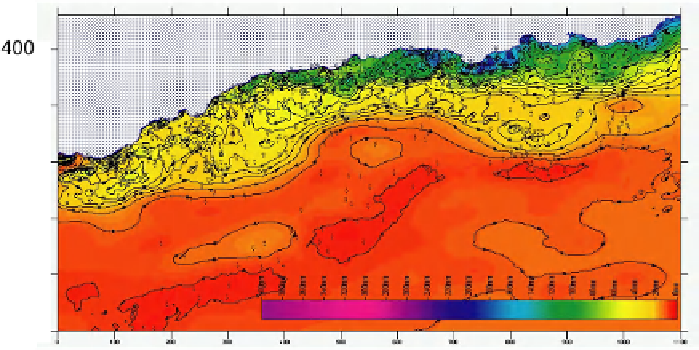
Figure 7.9.
Example of a map showing median rainfall values
for the month of December (see color section)
This method of creating 12 maps showing median monthly rainfall levels has
been used for a long time. For the purpose of our research we have focused on work
that was carried out by geographers who were based in the French city of
Strasbourg [SCH 77]. At that time maps had to be created manually. The technique
that is used today was first used in France in 1982 [LAB 82]. This modern technique
was quickly adopted, updated, and improved upon by the scientific community
[LAB 84; JOR 86; BEN 87]. Similar approaches were then used to measure other
climatic parameters, such as temperature, which is greatly affected by topography
[CAR 94]. Up until the 1990s, rainfall levels were estimated according to the
topographic factors that were used in the estimation process [LAB 95]. If too many
topographic factors are used to estimate rainfall levels, there is also an increase in
the number of redundant independent variables that are used in the estimation
process. If these topographic factors are used to estimate rainfall levels in large
areas (with a surface area of more than 500 km
2
), there is less focus on site effect
gauges. There is, however, more focus on the variations of the different topographic
factors used in the measurement process. Another area for consideration involves
the almost universal choice of the linear regression model. The altimetric gradient of
rainfall is not constant all over the world and because of this it has become
necessary to use non-linear equations. For some years now it has been clear that
there is a limited number of factors that affect rainfall levels; these variables include
altitude, distance from the sea, and distance from the crest of a mountain, etc [BER
00; KIE 01; DJE 01]. There is a general relationship that exists between rainfall
levels and relief [LAB 02], and between rainfall levels and distance from the sea
[ZAH 00].