Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
At larger flow rates, skimming flow occurs with formation of recirculat-
ing vortices between the main flow and the step corners. Air entrainment
occurs from the step edges. Downstream of the inception point, the flow
was highly aerated at each and every step with very significant splashing.
The flow direction of air-water mixture is almost parallel to the pseudo-
bottom formed by the step edges although shapes of the recirculating vor-
tices beneath the main flow alternate from step to step. Vortex begins at the
upper step and becomes developed at the subsequent downstream step. At
the stage of developing vortex, vortex formation is not clear and unstable.
Two or three vortices occur and disappear reciprocally. A smaller vortex
near the step corner is generated with flow direction opposite to the larger
one. Vortex formation is clear and stable at the stage of developed vortex.
Air entrainment was occurred mainly from behind the trailing edge of
the drop structure due to flow separation. Air bubbles were formed and pro-
ceed to downward direction becoming larger in volume, and finally become
broken and disappeared during proceeding upward. Abundant dissolved
oxygen was stored with breaking of the air bubbles and this would give
the good habitat condition, which is the same ecological feature as riparian
ries.
4
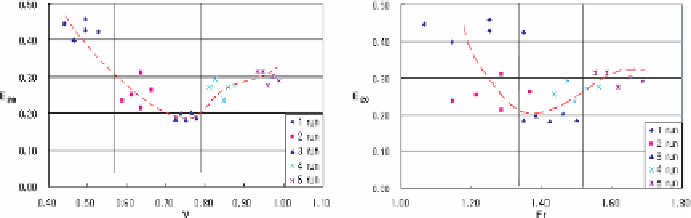
Figure 6 shows the relationship between the oxygen transfer by flow
characteristics. Flow condition changes from a nappe flow to a skim-
ming flow as the flow velocity and Froude number increase. The transi-
tion between nappe and skimming flow was shown to occur at region of
v
=0
.
56-0
.
79 (m/s) and
Fr
=1
.
32-1
.
51. This was due to the undular pro-
file of the free surface, acceleration above filled cavities and deceleration at
nappe impact as was suggested by Chanson and Toombes.
7
Oxygen transfer becomes smaller and reaches to minimum value at the
beginning stage of a skimming flow, but becomes larger in the region of
nappe flow
region
transition flow
region
skimming flow
region
nappe flow
region
transition
flow
region
skimming
flow
region
Fig. 6.
Relationship between oxygen transfer and flow parameters.