Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
2.5.3.
Interplanetary shocks
In-situ
observations of interplanetary shocks at 0.3-0.47 AU provide a
unique opportunity to identify different characteristics of more energetic
radio sources not observed at Earth.
3. Instrument Design
To meet the science objectives, PWI is designed as a sophisticated
plasma/radio wave receiver system with high sensitivity electric and mag-
netic sensors. The PWI has two pairs of electric field sensors, Wire-Probe
anTenna (WPT) and Mercury Electric Field
In-situ
TOol (MEFISTO) and
two types of magnetic field sensors, Low-frequency search coil (LF-SC) and
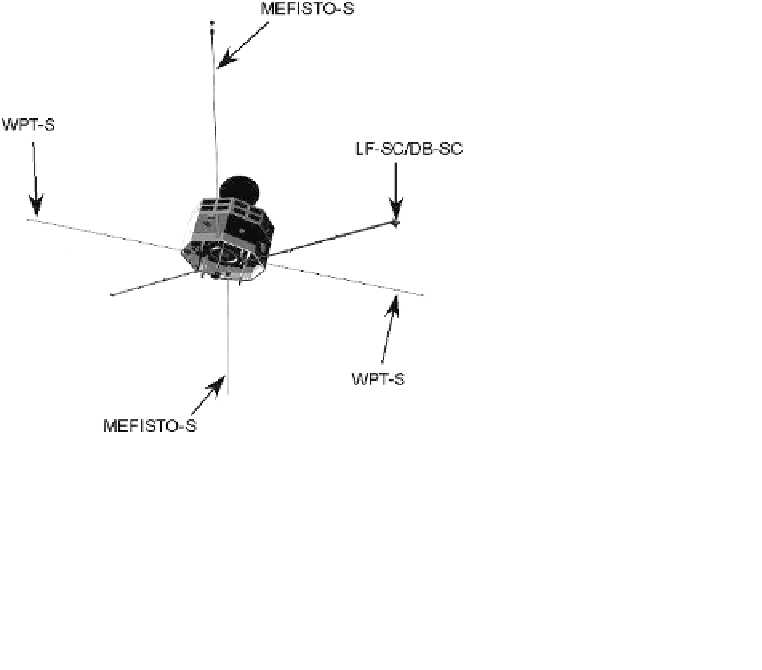
dual band search coil (DB-SC). The configuration of the PWI sensors is
shown in Fig. 2. (Note that MEFISTO and WPT consist of the sensor
units and their peripheral electronics such as the deployment system. We
address each sensor unit as MEFISTO-S and WPT-S, respectively.) Using
these sensors, the PWI covers a very wide frequency range, DC to 10 MHz
for electric field and 0.1 Hz to 640 kHz for magnetic field.
Fig. 2.
External view of the MMO spacecraft and PWI sensors.