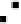Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
10
-3
10
-3
(a)
(b)
Spacewatch (inner)
SDSS (red)
R
10
-4
10
-4
Lunar highlands
crater projectiles
Lunar highlands
crater projectiles
0.1
1
10
0.1
1
10
10
-3
10
-4
(c)
(d)
NEAs (LINEAR)
Subaru
(inner)
R
10
-4
10
-5
Lunar highlands
crater projectiles
Mars younger
plains projectiles
0.1
1
10
0.1
1
10
D
[km]
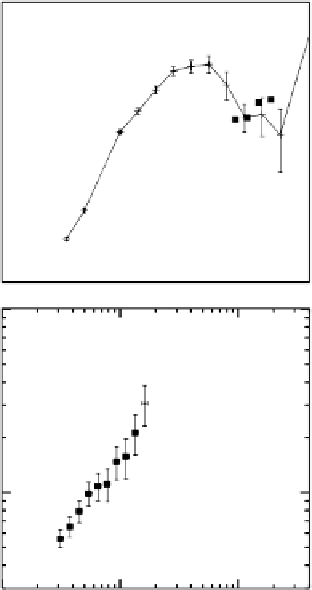
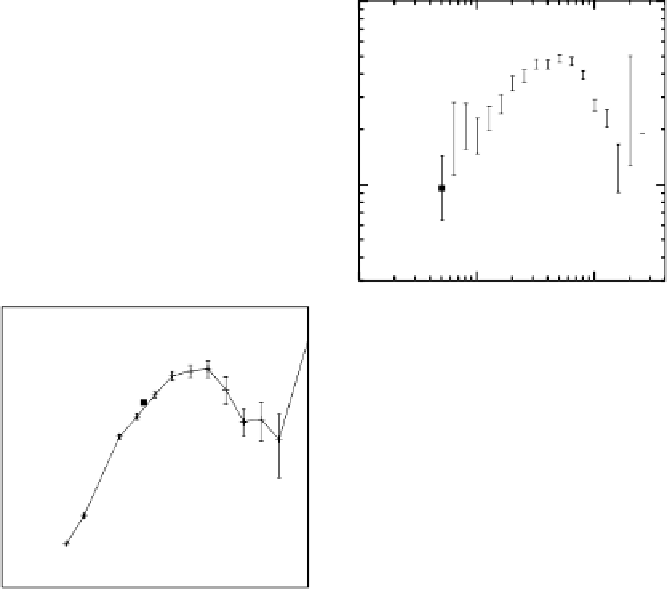
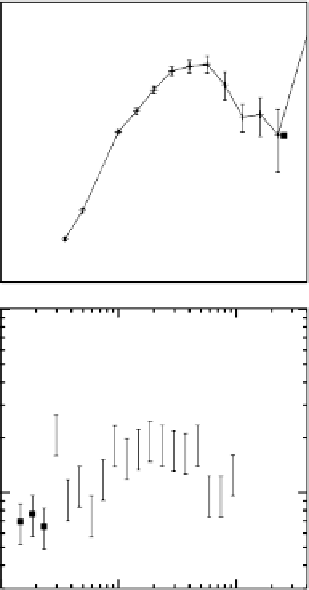
Fig. 2.
with error-
bars) and crater projectiles (solid lines with errorbars). (a)-(c) are for the oldest
lunar highlands crater projectiles and the MBAs mainly in the inner belt surveyed by
(a) Spacewatch,
7
(b) SDSS,
8
and (c) Subaru.
9
(d) is the comparison between the young
martian crater projectiles and NEAs surveyed by the LINEAR project.
10
Note that the
R
range is different in (d) from other panels.
Comparison between the SFDs of current asteroids (the symbol
planetesimals.
15
,
16
LHB occurred too late to invoke a nebula gas dissi-
pation as the cause of resonance sweeping, so the only alternative to pro-
voke the resonance sweeping is that the giant planets migrated at that
time due to interaction with a swarm of planetesimals. The planetesimal
disk must be massive enough to make giant planets radially migrate, hence
it should be a distant, massive planetesimal disk beyond the large plan-
ets. In addition, a mechanism is needed to produce a late start of giant
planet migration around 4 Gyr ago. One possible theory invokes the change