Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
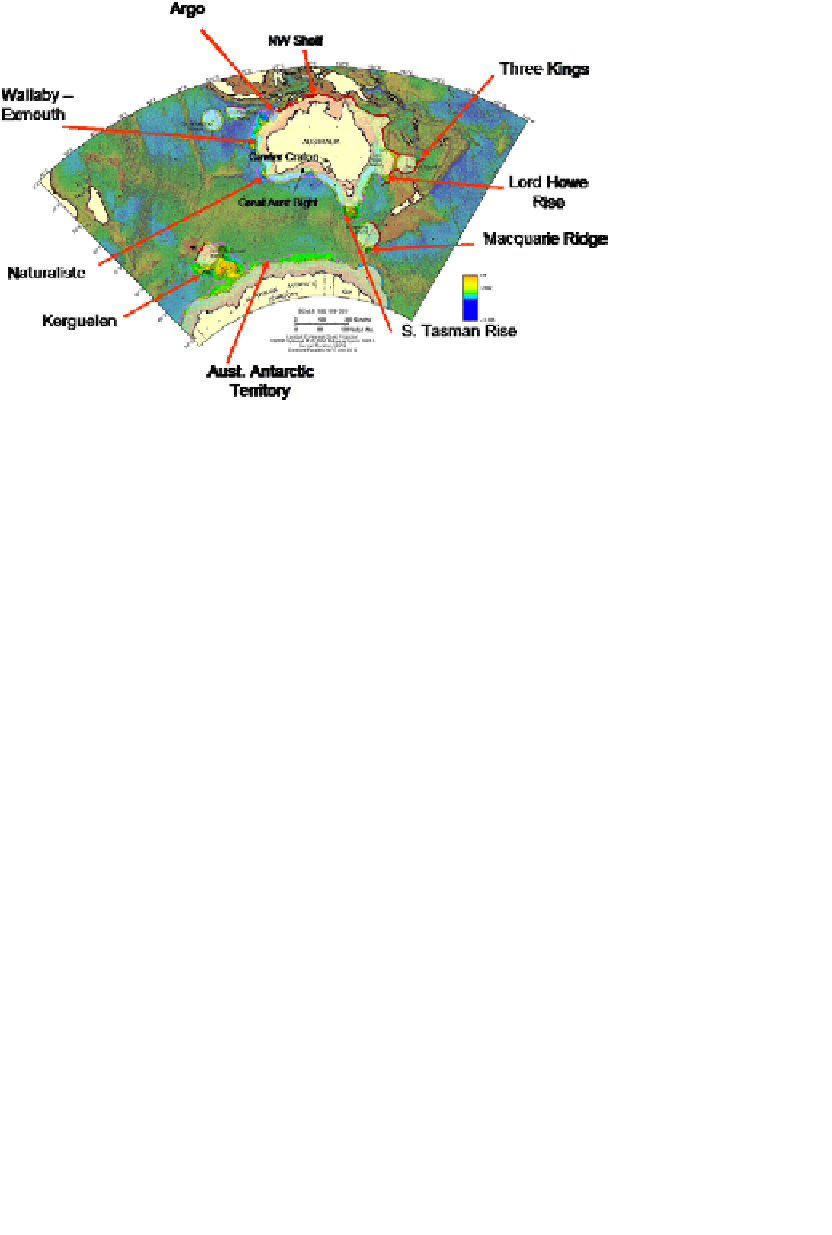
Fig. 1. Australia's maritime boundaries showing the areas of extended continental shelf
submitted to the UN Commission on the Limits of the Continental Shelf in November
2004,
10
and some areas of sulfide prospectivity.
present.
11
-
13
Plate reconstructions and palaeo-age grids for the Western
Pacific margin illustrate a number of back-arc basins associated with active
and remnant volcanic arcs systems including Norfolk Ridge, Loyalty-Three
Kings Ridge, Lau-Colville Ridge, and the Tonga-Kermadec Ridge.
14
,
15
By comparison with modern volcanic arc and back arc systems, the
Norfolk Ridge and Loyalty-Three Kings Ridge arc-back arc systems in
eastern Australian waters have potential to host submarine Cu-Zn-Au-
Ag massive sulfide deposits. Further work incorporating tectonic models
and observational constraints into 3D mantle convection models is pro-
viding important predictive tools for mineral exploration.
14
,
15
Zones of
reduced magnetization-often associated with volcanogenic massive sulfide
hydrothermal systems
16
are potential geophysical footprints with which to
explore for massive sulfides in this area.
4. Mississippi Valley-Type Deposits
Like volcanogenic copper-zinc deposits, Mississippi Valley-type lead-zinc-
deposits are also an important class of base metal deposit.
17
Most occur in
orogenic foreland settings. Bradley and Leach
18
have examined deposits in
collisional forelands and suggest that, tectonically, the passive foreland car-
bonate shelf environment of the Banda Arc collision zone off NW Australia