Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
0.4
0.3
0.
1
0
0.5
0
−0.5
0.4
0.3
0.
1
0
0.5
0
−0.5
0.4
0.3
1
0.5
0
0.5
0
−0.5
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
duration (wave periods)
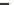
Figure 4.2 Simulations of steepness (first panel), skewness (second panel) and asymmetry (third
panel) of the wave of IMS
=
0
.
26 as it evolves from the initial conditions to the point of breaking.
Top three panels:
U
/
c
=
2
.
5; middle three panels:
U
/
c
=
5
.
0; bottom three panels:
U
/
c
=
10
.
0
However, the instability causes gradually increasing instantaneous distortions of the wave
shape, such that at some point the water surface can apparently no longer sustain the wave
profile, and collapses. It should be noted that comparisons of such numerical simulations
with experiments can only be qualitative. At the initial stages of development, the necessary
instability modes, if they are absent, should grow from the continuous background noise
(e.g.
Reid
,
1992
;
Babanin
et al.
,
2007a
,
2010a
). Such noise is essentially suppressed in a
discretised numerical model, particularly if the model is very precise, which fact delays the
instability onset.
Figure 4.2
shows a simulated evolution of the nonlinear wave properties to the point
of breaking in the presence of wind forcing. As above, in each set of three panels the top
panel shows the evolution of individual wave steepness, middle panel - wave skewness, and
bottom panel - asymmetry. Three sets of subplots correspond to three wind-forcing condi-
tions:
U
0(very
strong forcing) where
U
is a characteristic wind speed at a characteristic half-wavelength
height (the model is non-dimensional and therefore there is no standard 10m height and
respective wind
U
10
). The initial steepness chosen is IMS
/
c
=
2
.
5 (moderate forcing),
U
/
c
=
5
.
0 (strong forcing) and
U
/
c
=
10
.
26, which should lead to a
faster evolution to breaking onset. No initial modulations were imposed. Note that the min-
imum value plotted on the steepness scale is
=
0
.
=
0
.
25 and not zero, and that the simulation
starts from a harmonic wave with
S
k
=
A
s
=
0.

























































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search