Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
A
B
C
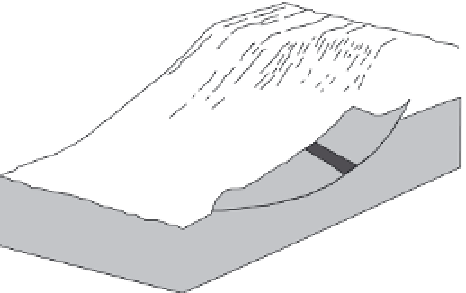
Figure 7.1.
Examples of three types of landslide. A
=
translational block slide,
B
=
rotational slump, C
=
earth flow (after Jibson and Keefer,
1994
).
Falls occur frequently and generally describe an event where the moving mass
travels mostly through air in free fall, saltation or rolling. In a rock fall, where a
single block or blocks of rock detaches from the rock face, the individual com-
ponents of the fall behave mainly independently of each other. Often there are
no movements that precede such falls and the process itself is very rapid. Inde-
pendent blocks increase in kinetic energy as the acceleration increases during
thefall. The blocks accumulate at the bottom of the slope as a scree deposit.
Freezing and thawing is one of the major processes that can result in rock falls.
Toppling failure is also classified as a fall. The risk of toppling increases with
increasing discontinuity angle. The discontinuity angle is the angle of a joint
or fracture which separates the blocks from the rock mass. Toppling failures
frequently occur on steep slopes of vertically jointed rocks.

















Search WWH ::

Custom Search