Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Eastern Mediterranean have been explained by long term episodic and continuous
GPS observations (Reilinger et al., 2006; Reilinger, 2000) some special cases need to
be defi ned in specifi c regional deformations. Izmir as a high populated city settled on
seismically active faults. Thus, there is always high seismic risk underlined in many
studies (Aktug and Kilicoglu, 2006; Kreemer and Chamot-Rooke, 2004; Nur and
Cline, 2000; Ocakoglu et al., 2005; Ozcep, 2000; Zhu et al., 2006) in Izmir, like the
North Anatolian Fault Zone.
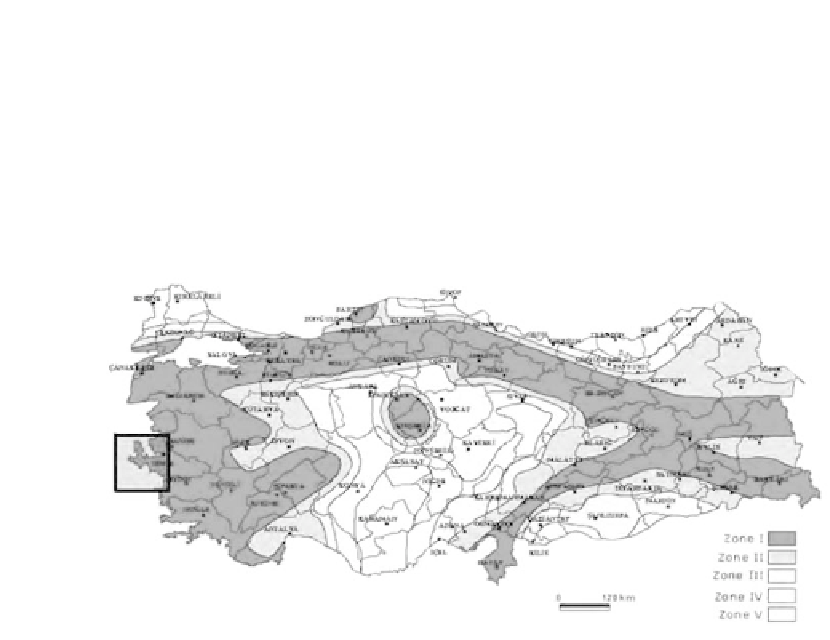
Figure 2.
Turkey earthquake hazard map and study area (Ozmen et al., 1997).
Several GPS network optimization studies have also been published during the last
decade (Blewitt 2000; Gerasimenko et al., 2000; Wu et al., 2003). Therefore, there is
a need to perform a large scale crustal deformation monitoring study using the results
of previous studies mentioned above, in order to evaluate regional tectonics. How-
ever, the tectonics of Izmir and its vicinity is very complex in the geological sense
and should be investigated in detail to understand long and short term geodynamic
activities.
The deformation pattern in the Mediterranean region which forms a low elevated
part of the Alpine Himalayan belt is rather complex, and usually occurs in the conti-
nental collision zones. The Aegean region is bounded to the north by the stable con-
tinental Eurasian plate, to the west by the Adriatic region, to the east by the central
Anatolian plate, and to the south by the oceanic material beneath the Mediterranean
Sea, which is northern edge of the African plate. The Black and Mediterranean Sea
fl oors have mean depths of 1,500 and 1,300 meters, respectively, while the Aegean Sea
fl oor has a mean depth of 350 m. In other words, the Aegean Sea fl oor may be seen as a
high plateau between the deeper Black Sea and Mediterranean Sea fl oors. The Aegean
is characterized by a relatively thicker crust (2,530 km) than a typical oceanic crust,
which might conversely be interpreted as a thinned continental crust. The Aegean is