Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Sun
A
A
′
A
″
S
B
O
Earth
Shadow
cast
A
″
∗
Vertical
gnomon
A
′
∗
∗
1/50th of a circle
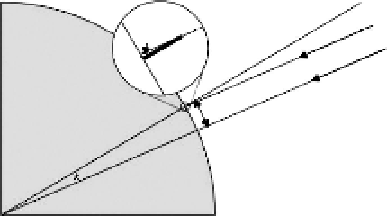
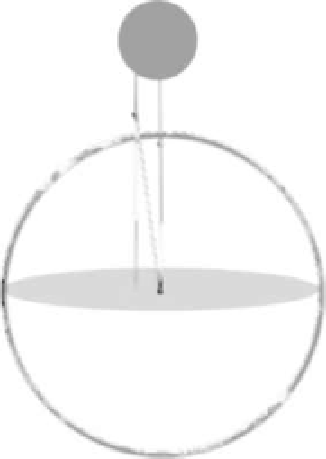
Figure 2.1 Eratosthenes's measurement of the circumference of the Earth, based on a
theorem of Euclid. In the top image, the Sun is shown as a small gray ball far away
from the Earth (large ball). The Sun's rays are assumed parallel to each other as
they strike the Earth's surface. The bottom image shows the detail of the configura-
tion of obelisk (gnomon) and shadow in relation to the surface of the Earth.
• Assume the Earth is a sphere.
• The circumference of the sphere is measured along a great circle
on the sphere.
• Find the circumference of the Earth by inding the length of inter-
cepted arc of a small central angle.
• Find two places on the surface of the Earth that lie on the same
meridian (or close to it): Meridians are halves of great circles.
• Eratosthenes chose Alexandria and Syene, near contemporary
Aswan (
A
′
and
S
in Figure 2.1, respectively).
• Assume that the rays of the Sun are parallel to each other.
• The Sun's rays are directly overhead, on the summer solstice (c.
June 21), at 23.5 degrees north latitude.
• Syene is located at about 23.5 degrees north latitude. Hence, on
the summer solstice, sunlight will pass to the bottom of a narrow
well (and it will not do so on other days),
S
.

Search WWH ::

Custom Search