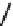
Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Zone of 2-D
Soil-Pipeline
Interaction
Zone of
Ground
Rupture
Pipeline
Zone of
Grond
Rupture
Landslide or
Zone of Lateral
Spread
Fig. 17.3. Schematic ofsoil-pipeline interaction for landslides and/or lateral spread
complex. As will be discussed in a forthcoming section of the paper, the lateral forces
mobilizedagainstthepipenearthegroundruptureplaneinvolvethree-dimensional(3-D)
soil failureand interaction withthe pipeline.
3. Lifeline system response to earthquakes
The 1994 Northridge earthquake caused the most extensive damage to a US water sup-
ply system since the 1906 San Francisco earthquake. Three major transmission systems,
which provide over three-quarters of the water for the City of Los Angeles, were dis-
rupted.LosAngelesDepartmentofWaterandPower(LADWP)andMetropolitanWater
District(MWD)trunklines(nominalpipediameter
600mm)weredamagedat74loca-
tions, and the LADWP distribution pipeline (nominal pipe diameter
≥
<
600mm) system
was repaired at 1013 locations.
The earthquake-induced damage to water pipelines and the database developed to char-
acterize this damage have been described elsewhere (O'Rourke et al., 1998, 2001; Jeon
and O'Rourke, 2005), and only the salient features of this work are summarized herein.
GIS databases for repair locations, characteristics of damaged pipe, and lengths of trunk
lines according to pipe composition and size were assembled with ARCView software.
Nearly 11,000km of distributionlines and over 1,000km of trunk lines were digitized.
Figure 17.4 shows the portion of the Los Angeles water supply system most seri-
ously affected by the Northridge earthquake superimposed on the topography of Los
Angeles. The figure was developed from the GIS database, and shows all water sup-
ply pipelines plotted with a geospatial precision of
±
10m throughout the San Fernando