Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
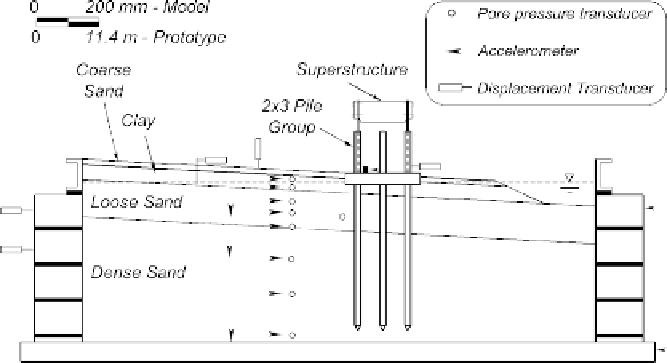
Fig. 12.2. Centrifuge model with a superstructuresupported bya pilegroup
embedded inprofile that develops lateral spreading during shaking (most sensors
omitted for clarity)
typical set of recording data shown in Figure 12.3, with much of the movement develop-
inginalocalizedshearzoneattheinterfacebetweentheliquefiedsandandtheoverlying
clay. Thus, the timing of lateral spreading displacements can be affected by the numer-
ous factors that affect the diffusion of earthquake-induced excess pore water pressures.
For design purposes, it is prudent to assume that a significant portion of the final lateral
spreading displacements occur during strong shaking, such that the lateral spreading and
inertia demands can be additive.
The transient lurching of liquefied ground during strong shaking can produce significant
kinematic loading in the direction transverse to the primary direction of lateral spread-
ing and at level sites that are far from a free face and not prone to lateral spreading.
The lateral displacements during ground lurching are generally smaller than the perma-
nent displacements associated with lateral spreading, but they can still be large enough
toimposesubstantialdemandsonpilefoundations.TokimatsuandAsaka(1998)suggest
thattheamplitudesofcyclicgrounddisplacementscanbeestimatedbyintegratingpoten-
tial cyclic shear strain profiles, in a way that is similar to that used for estimating lateral
spreading displacements. They present relationships that suggest the cyclic shear strains
during ground lurching may be estimated as about 10%-20% of the maximum potential
shear strainsused forestimating permanent lateral spreading displacements.
2.4. ANALYSIS OFPILES FOR THELIQUEFACTION CASE
2.4.1. Modify the BNWF model for the effects of liquefaction
The BNWF analysis for the liquefaction case requires the application of soil displace-
ments to the free-field ends of the p-y springs in addition to the application of inertia
loads as illustratedin Figure 12.4(a).