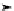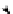Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Footing displacement zero
250
250
a
b
200
200
Footing
action
Footing actions
150
150
100
100
50
50
0
0
Footing width
Footing width
Fig. 10.13. Bearing pressure distributionbeneath a shallow rigidstripfoundation on a
nonlinear soil.(a) Pressure distributionunder a vertical load corresponding to
V
/
33. (b) Bearing pressuredistributionunder the vertical load in(a) with
moment superimposed (themagnitude of themoment issuch that thevertical
displacement ofthe right hand edge of thefooting just reaches zero)
V
uo
=
0
.
In Figure 10.13a the distribution of vertical pressure beneath the footing is plotted at a
verticalloadatwhich
V
33.ComparingFigures10.11aand10.13a(andmaking
due allowance for the fact that Figure 10.9 is for a square footing whilst Figure 10.11 is
for a strip foundation, and that the undrained shear strength of the soil in Figure 10.11 is
100kPa and that of Figure 10.13 is 50kPa) it is apparent that the nonlinear stress-strain
behaviour of the soil means that although the concentration of vertical stress at the edge
of the footingisstill apparent itisnot as sharp as inthe elastic case.
ThenextstepintheFLACmodellingistoapplysomemomentloading.Firstthefooting
istakentothe“working”verticalloadandthen,whilekeepingtheverticalloadconstant,
somemomentisappliedtothefooting.Theeasiestwaytoapplytheseloadsisbyimpos-
ing displacements at the nodal points and evaluating the applied actions from the nodal
forces. For the vertical loading of the rigid footing uniform vertical displacements are
imposed, whilst for the subsequent moment loading an additional displacement profile
is applied which has a linear downward displacement on one side of the footing and an
upward displacement on theother, but zero vertical movement at the centre.
/
V
uo
=
0
.
The pressure distribution beneath the foundation on a nonlinear soil is shown in
Figure 10.13b. It is of note that at this point the vertical displacement of the footing
edge is zero (that is the upward rotational displacement is equal to the downward ver-
tical displacement at the commencement of the moment loading). This is an interesting
demonstration of how the simple spring model does not represent what is occurring
beneath the footing - if the spring model was used then the reaction pressure at the edge
of the foundation at that moment would be zero.