Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
100
80
60
Elastic continuum
40
20
Discrete springs
0
0
5
10
15
20
Footing length (m)
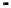
Fig. 10.10. Ratioof the rotational tovertical stiffness ofsquare rigidshallow
footings, fora uniformelasticfoundation material and thefoundation represented
as abed of discrete springs
foundation on a bed of springs is considerably less than that when the foundation is on a
continuous elastic material.
The explanation of this difference is apparent if one considers the reaction pressure dis-
tribution beneath these foundations. For the bed of springs at every point the reaction
pressure depends only on the displacement at that point. So for uniform vertical dis-
placement ofarigidfoundation therewill be auniform reactionpressure.Similarlyfora
rotationaldisplacementofafoundationonthebedofspringsthereactionpressuredistri-
bution will be linear following the spring displacements. However for a rigid foundation
on a continuous elastic material the reaction pressure distribution is not uniform for a
uniform settlement. The pressure tends to be very large at the edges. The reason for this
is that the strains imposed on the soil are very large at the edges of a rigid foundation.
Furthermore the pressure at any point beneath the foundation influences the pressure at
every other point beneath the foundation. The calculated pressure distribution for uni-
form vertical displacement of a rigid square footing and is plotted in Figure 10.11a. The
vertical load applied to the foundation resting on saturated clay with an undrained shear
strengthof100kPaissuchthat
V
33.Thecalculationwasdoneusingthewell-
known solution for the vertical displacement of the surface of an elastic half-space when
a pressure loading is applied over a rectangular area (cf, for example, Poulos and Davis,
1974). In a similar manner the pressure distribution when the foundation is subject to
moment can be calculated. The distribution when the foundation is subject to moment
superimposed on the vertical loading is plotted in Figure 10.11b. The magnitude of the
/
V
uo
=
0
.