Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
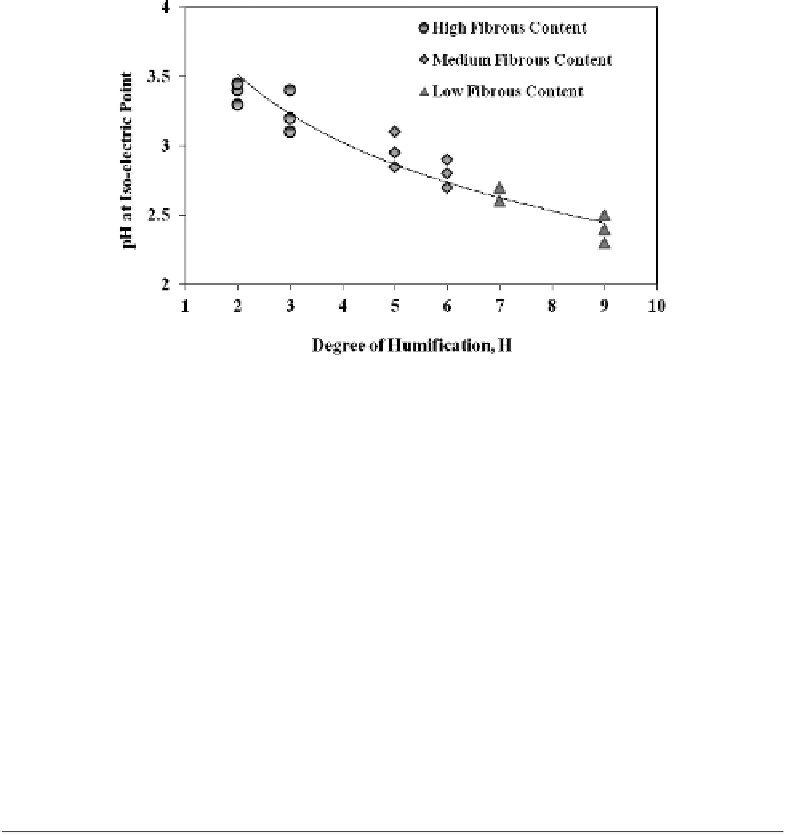
Figure 3.18
pH at iso-electric point vs. von Post degree of peat humification (
after Asadi et al.
, 2009d).
Table 3.8
Zeta potential of very slightly decomposed peat (
after
Asadi, 2010).
Hydrated
Cation
Concentration
Zeta potential
Cation
radius (nm)
valence
(mol L
−
1
)
pH
(mV)
Na
0.36
1
1.00E-02
3.04
−
7.1
1.00E-02
9.1
−
19.9
1.00E-02
10.46
−
25.23
1.00E-04
3.04
−
6.7
1.00E-04
10.2
−
24.2
Ca
0.41
2
1.00E-02
3.42
−
2
1.00E-02
7.42
−
9.3
1.00E-03
3.5
−
3.7
1.00E-04
9.65
−
11.3
1.00E-04
11.2
−
14.4
Al
0.48
3
1.00E-03
7.54
−
3.1
1.00E-03
11.63
−
17.2
1.00E-04
11.77
−
22.8
the pH effects can possibly be ascribed to dissociation of H
+
from the functional
groups. Many carboxylic groups are sufficiently acid to dissociate below pH 6 leaving
a negative charge on the functional group:
COO
−
+
H
+
R
−
COOH
=
R
−
(3.10)
R represents organic species whose differing electronegativities change the tendency for
H
+
to dissociate. Thus the various R-COOH units dissociate at different pH values.
As the pH of the system increases, still weaker carboxylic groups and other very weak
acids dissociate (Stevenson, 1994).