Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
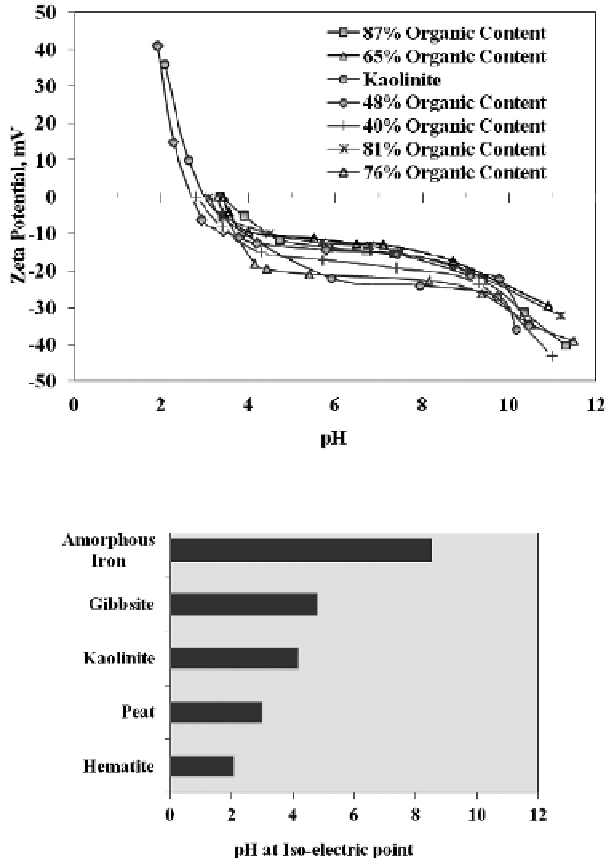
Figure 3.15
Zeta potential vs. pH (
after
Asadi
et al
., 2009d).
Figure 3.16
pH at iso-electric point of peat in comparison with some minerals (
after
Asadi
et al
., 2009d).
At a certain pH, the soil surface charge could drop to zero, rendering a zero
ζ
,or
what is called the iso-electric point (Lorenz, 1969). The peat surface charge drops to
zero
ζ
at pH 2.5 to 3.5 (Figure 3.15).
Figure 3.16 shows the values of the iso-electric point of some minerals in compari-
son with peats from this study (Mohamed and Anita, 1998). Since all charge in humus
is strongly pH-dependent, the sensitivity of organic soils to pH changes is greater than
that of mineral soils. Despite this high sensitivity, the iso-electric point of organic soils
is less than that of amorphous iron, gibbsite and kaolinite.