Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
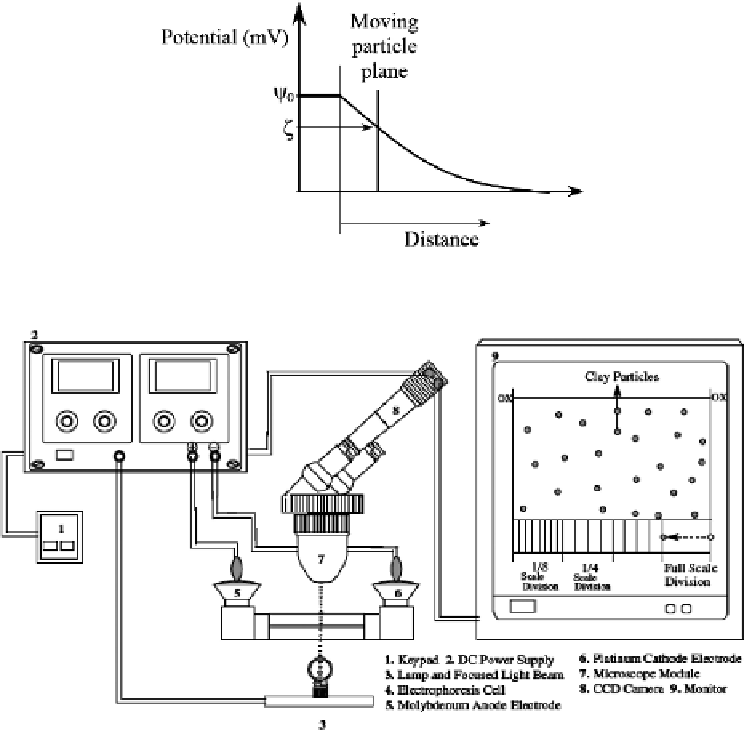
Figure 3.13
Potential distribution showing the slipping plane (zeta) potential (
after
Mitchell and Soga,
2005).
Figure 3.14
Arrangement of Zeta-Meter 3.0
+
Unit (
after
Zeta-Meter System 3.0 Operating Instruc-
tions).
µ
through a #100 (150
m) sieve. For each sample, a solution of 0.15 to 0.2 g/L of the
pretreated soil in 0.0001M NaCl can be prepared.
ζ
is measured with a zeta-meter as a function of pH values. A zeta-meter is a
microprocessor-based instrument (shown schematically in Figure 3.14). The unit auto-
matically calculates the electrophoretic mobility of the particles and converts it to
the zeta potential using the Smoluchowski equation, which provides a direct relation
between the zeta potential and electrophoretic mobility.
The measurement of Zeta Potential is important in understanding the electrical
charge characteristics of sample particles. The electrical charge properties control
the interactions between particles and therefore determine the behaviour of the soil
particles.
All measurements are usually made in 0.0001 M NaCl solutions and pH
adjustments are made using dilute HCl or NaOH solutions (West and Stewart, 1995).