Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
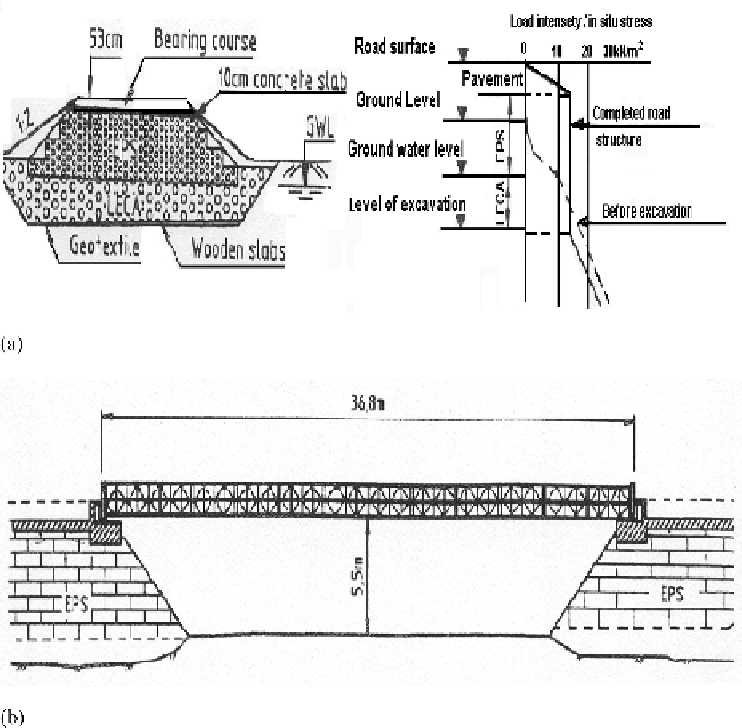
Figure 6.36
Examples of EPS applications. (a) As compensated foundation; (b) support for bridge
abutment; (c) arrangement of lightweight polystyrene blocks at culvert transition; and (d)
section view of culvert transition (
after
Gan and Tan, 2003).
By excavation and replacement with the polystyrene blocks, it is theoretically
possible to completely float the embankment, thus imposing zero net stress to the
underlying ground. This technique is also known as 'weight credit construction'. An
interesting aspect of this construction is the need to have a stable water table, as
any changes will alter the state of buoyancy and potentially caused movement in the
systems. The blocks need also to be protected from fire, usually by mean of earth cover
and top concrete slabs. A general review of the literature on the use of EPS is provided
by Frydenlund and Aaboe (1997), Horvath (1995) and Gan and Tan (2003). Figure
6.36 illustrates some of their application examples.
Lauritzsen and Lee (2002) suggested that it is possible to use EPS as a foundation
for building two-storey houses and garden directly on peat, in addition to road.