Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Peak value =
1.414
rms = 0.707
peak
av = 0.637
Peak
value
rms
value
av
value
+
Peak-to-
peak value
0
90°
180°
360°
270°
-
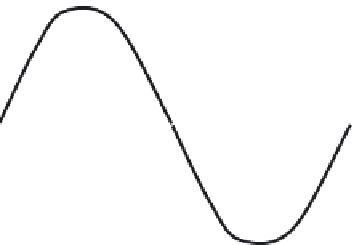
FIGURE 11.57
Amplitude values for AC sine wave.
11.7.11.6 Peak-to-Peak Amplitude
A second method of indicating the amplitude of a sine wave consists of determining the total volt-
age or current between the positive and negative peaks. This value of current or voltage is the
peak-to-peak value
(see Figure 11.57). Because both alternations of a pure sine wave are identical,
the peak-to-peak value is twice the peak value. Peak-to-peak voltage is usually measured with an
oscilloscope, although some voltmeters have a special scale calibrated in peak-to-peak volts.
11.7.11.7 Instantaneous Amplitude
The
instantaneous value
of a sine wave of voltage for any angle of rotation is expressed by the fol-
lowing formula:
e
=
E
m
× sinθ
(11.49)
where
e
= Instantaneous voltage.
E
m
= Maximum or peak voltage.
sinθ
= Sine of angle at which
e
is desired.
Similarly the equation for the instantaneous value of a sine wave of current is
i
=
I
m
× sinθ
(11.50)
where
i
= Instantaneous current.
I
m
= Maximum or peak current.
sinθ = Sine of the angle at which
i
is desired.
Note:
The instantaneous value of voltage constantly changes as the armature of an alternator
moves through a complete rotation. Because current varies directly with voltage, according
to Ohm's law, the instantaneous changes in current also result in a sine wave whose positive
and negative peaks and intermediate values can be plotted exactly as we plotted the voltage
sine wave. Because instantaneous values are not useful in solving most AC problems, an
effective value is used instead.











Search WWH ::

Custom Search