Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
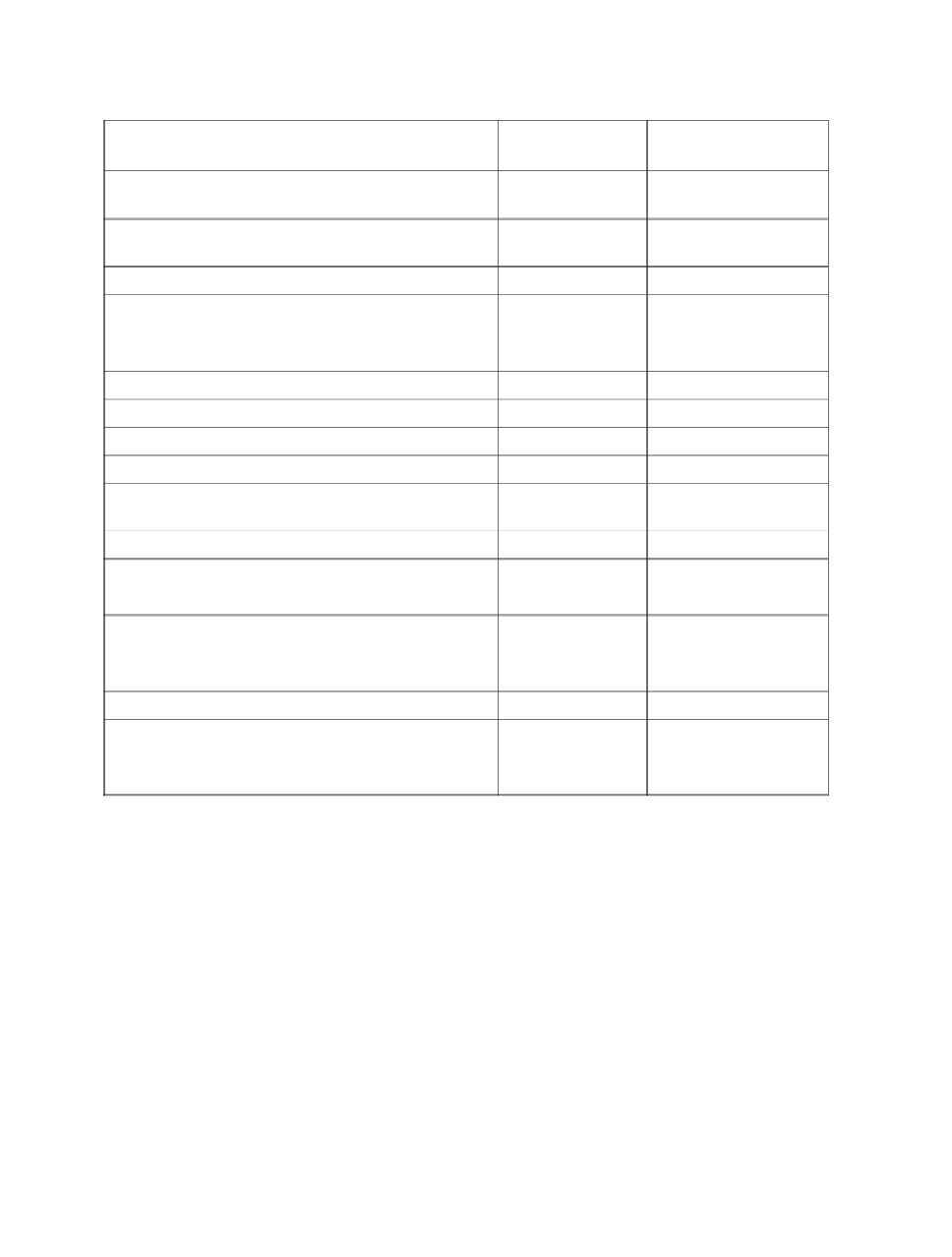
Table 14
Sulphur containing fertilisers
(Source:
Soil Sense
C-04)
Carrier
Chemical formula
Per cent sulphur
1 kg/ha of S requires:
(kg of fertiliser)
Ammonium phosphate
sulphate
Varies
10 -14
7.2-10
Ammonium
polysulphide
Varies
36-45
2.2-2.8
Ammonium sulphate
(NH
4
)
2
SO
4
23.7
4.2
Ammonium
thiosulphate
(NH
4
)
2
S
2
O
3
26 (60% aqueous)
3.9
Copper sulphate
CuSO
4
12.8
7.8
Epsom salts
MgSO
4
.7H
2
O
14.0
7.2
Iron sulphate
Fe SO
4
11. 5
8 .7
Gypsum
CaSO
4
2H
2
O
18.6
6.0
Manganese sulphate
MnSO
4
14.5
6.9
Potassium magnesium
sulphate
K
2
SO
4
2MgSO
4
22.0
4.6
Potassium sulphate
K
2
SO
4
17-18
5.6
Sulphur, elemental
S
30-100
1.0-3.4
Sulphur dioxide
SO
2
50
2.0
Sulphuric acid
(100% H
2
SO
4
)
32.7
3.1
Superphosphate,
normal
Ca(H
2
PO
4
)
2
+CaSO
4
2H
2
O .9
.4
Superphosphate, triple
Ca(H
2
PO
4
)
2
+CaSO
4
2H
2
O .4
.4
Urea ammonium
sulphate
Varies
4-13
7.7-25
Zinc sulphate
ZnSO
4
H
2
O
18
5.6
Note 1.
Most sulphur fertilisers containing nitrogen tend to acidify the soil, so soil pH should be monitored
regularly if using these fertilisers. Generally, for each kg of sulphur applied, 4 kg of lime will be needed to
neutralise the acidifying effect. Elemental sulphur is particularly acidifying.
Note 2.
Copper, manganese and zinc are trace elements, and as such will have an effect on the soil as well as the
sulphur in the sulphate part of these fertilisers. These materials should be used with care.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search