Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Various other shapes have been worked out, e.g. line or strip load (Flamant) and
arbitrary shape (Newmark). Westergaard elaborated elastic solutions for
anisotropic soils (limited horizontal deformation), which gives stresses less than
Boussinesq. The reality may be in between. Deformations in layered non-linear
subsoils are more complicated and numerical computation is the only possible way.
Pile deflections behave non-linearly (see Fig 12.5). Fahey and Carter suggested a
practical method for the vertical pile settlement, based on elastic continuum theory,
by adding a factor (1
q/q
u
)
0.3
related to the degradation of the elastic modulus
with increasing strain. In this regard, the vertical deformation
w
of a pile under
axial loading
Q
becomes
q/q
u
)
0.3
QI/
(2
r
0
E
e
)
w =
(1
(12.24b)
Here,
I
is an empirical factor (see Mayne, Poulos, Randolph), and
E
e
is the
equivalent elastic modulus along the pile at the toe. Piles when installed may be
subjected to horizontal forces due to inclined loading or deformations of the soil
they are placed in. This topic is not further elaborated in this topic.
D
DYNAMIC SOIL RESPONSE
Soil response to vibrations
The dynamic soil response under shaking or rocking loading can be represented
by a set of springs and dashpots. Several methods have been developed, such as
elastic half space theory, a cone model, analytical solutions, and dynamic finite
element methods, each with its limitations. Sophisticated tests have been
undertaken to validate the methods. Here, we consider the cone model, developed
by Ehlers (1942) for homogeneous subsoils.
h
Q
0
Q
0
r
0
w
0
M
w
0
z
c
Q
k
dz
r
w
Q + Q
,z
dz
(a) Ehlers' model (b) mass-spring-dashpot model
Figure 12.8
The harmonic vertical displacement
u
of a rigid mass-less circular foundation
disk with radius
r
0
and surface
A
0
=
r
0
2
on the surface of a homogeneous soil is
addressed (Fig 12.8a). The cone, expanding with depth with apex
, has a cross-
r
2
, increasing with depth proportional to
z
2
. At depth
z
the induced
section
A =



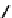
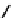

















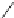

















Search WWH ::

Custom Search