Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Plastic wedge
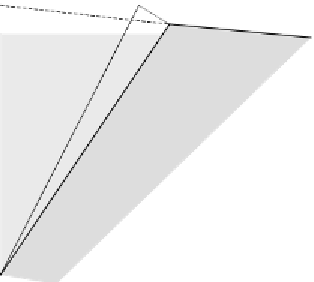
An important element of a steady visco-plastic motion with an analytical
solution is the plastic wedge as shown in Fig 9.7. During a small rotation
,t
dt
the
wedge OAB is assumed to undergo a full plastic deformation and it moves into
shape OA'B', while the outside remains rigid. Along the interface OB” a slip takes
place, proportional to
s
, in fact B”B'=
is
determined by considering volume constrained plastic deformation: area OAB
equals area OA'B'. For convenience, the angle
h/
cos
, and P”P'=
s
. The factor
/2, without
loss of practicality. Compatibility along the interface requires (see Fig 9.7)
is restricted: 0
<
<
as = s
,t
cos
s
sin
and
bs = s
,t
sin
s
cos
(9.32)
y
A
s
,t
cos(
)
B
P
B”
A'
B'
P
P”
P'
h
bs
s
s
sin(
)
P”
s
cos(
)
as
s
,t
P'
s
,t
x
O
s
sin(
)
Figure 9.7 The plastic wedge
The displacements in the wedge are expressed by
u
x,t
= ax/
sin
and
u
y,t
=
by/
cos
(9.33)
Elaboration of the volume constraint condition yields
s
2
cos
= s
2
(cos
V
OAB
= V
OA'B'
sin
b
)(sin
a
)
a
cos
b
sin
= ab
0
,t
cos
2
,t
sin
2
sin
cos
cos
sin
=
0
,t
(cos
2
sin
2
=
)/(2sin
cos
)
=
=
,t
cos(2
)/sin(2
)
=
,t
cotg(2
)
(9.34)
And consequently











































Search WWH ::

Custom Search