Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
For sand the Matsuoka-Nakai model is a modification between the Drucker-
Prager criterion and the Mohr-Coulomb rule, and it is convenient for other stress
paths than triaxial.
The Hardening Soil model (Vermeer c.s.) involves friction hardening to model
the plastic shear strain in deviatoric loading and cap hardening to model the plastic
volumetric strain in primary compression (see equations 9.7). Failure is defined
according to Mohr-Coulomb. The model covers reduction of mean effective stress
and mobilisation of shear strength. Soil dilation is covered and a power law
formulation for stiffness is applied (Duncan-Chang model). This model can be used
to accurately predict displacement and failure for general types of soils in various
geotechnical applications. The model does not include anisotropy or creep.
1
1
1
a
a
a
a
a
a
1
1
1
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
b
b
b
a
a
a
b
b
b
b
b
b
1
1
1
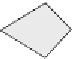
Figure 9.3 Concept of double sliding along Coulomb shear planes
The concept that the flow of granular materials is governed by shear on critical
surfaces can be used to formulate an elastic-plastic model. When the elastic strains
are neglected, i.e. for large strains, the model becomes identical to the rigid-plastic
model of de Josselin de Jong, which he named the Double Sliding model. For the
critical surfaces, he adopted the conjugate shear planes of the Mohr-Coulomb
model. A typical deformation according to rigid-plastic double sliding is shown in
Fig 9.3.
85°
85°
85°
88°
88°
88°
88°
94%
94%
94%
94%
100%
100%
100%
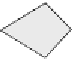
Figure 9.4 Difference of Mohr-Coulomb (left) and Double Sliding (right)
When compared to the non-associative Mohr-Coulomb model (Fig 9.4) it is
shown that the rotations and displacements are somewhat different (Teunissen).
The Double Shearing model predicts in general lower limit loads, because, for a




























































































































































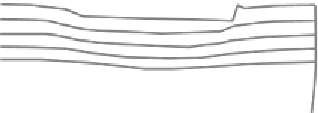















































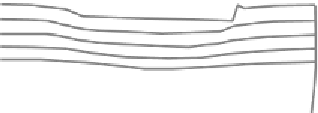




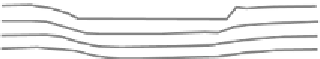













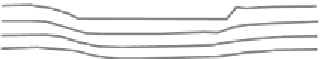






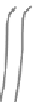










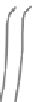


























Search WWH ::

Custom Search