Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
When loading is not isotropic and shear stress is involved, the situation differs.
Accounting for density changes during shear, equation (7.15) can be approximately
extended to
v
=
'/K - D
(7.17)
where
D
represents a dilation parameter, i.e. a relation between shear stress change
and corresponding volume strain. For
D
> 0, a volume increase (dilatancy) occurs
and for
D
< 0 a volume decrease (contraction), see Fig 7.1. Using (7.14) and (4.1b),
equation (7.17) gives
u = B
(
- KD
)
(7.18)
Conditions in a triaxial cell test can be expressed by
p =
=
(
1
+ 2
3
)/3
=
3
+
(
1
-
3
)/3
and
2
=
1
-
3
=
q
(7.19)
Here,
3
is the cell pressure and
1
-
3
the vertical load step, both typical
triaxial test items. (7.19) render (7.18) into
u = B
(
3
+ A(
1
-
3
))
with
A =
( - ½
KD
)
(7.20)
Although
A
and
B
are not intrinsic soil parameters, they reflect effects of pore
water compressibility and soil dilation, in an approximate way. It also shows that
under triaxial conditions the loading is only partly related to the pore water.
Expressed in terms of
p
and
q
equation (7.20) becomes
q KD
).
Hence, in an undrained triaxial test, for incompressible pore water (
B
= 1) and no
dilation (
D
= 0
)
,
u = B
(
p -
½
u
=
0. In a
p-q
diagram it shows a stress path under a
slope of 1/3 (DC in Fig 7.6). In a
p'-q
diagram, it corresponds to a vertical effective
stress path. When the soil is loose, i.e.
D <
0,
p'
=
p -
u
will be larger and the effective
stress path will incline to the left (DU in Fig 7.6)); for compressible water (
B
< 1)
or dense soil (
D >
0) the stress path will turn to the right (DU' in Fig 7.6).
1
+
3
1
+
3
1
+
3
1
+
3
1
+
3
due to deviatoric
deformation
due to deviatoric
deformation
due to deviatoric
deformation
due to deviatoric
deformation
due to deviatoric
deformation
t
t
t
t
t
S
0
S
&
S
0
S
&
S
0
S
0
S
0
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
due to isotropic and
deviatoric deformation
due to isotropic and
deviatoric deformation
due to isotropic and
deviatoric deformation
due to isotropic and
deviatoric deformation
due to isotropic and
deviatoric deformation
S
&
S
&
S
&
Settlement
Settlement
Settlement
Settlement
Settlement
(a) (b) (c)
Figure 7.8 Settlement in a triaxial cell test and at the edge of a land fill



































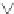









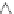
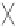




















Search WWH ::

Custom Search