Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
1.2
Interaction of the Radiation and the Atmosphere
Consider a symbolic particle (a gas molecule, an aerosol particle) that is
illuminated by the parallel beam
F
0
(Fig. 1.4). The process of the interaction
of radiation and this particle is assembled from the
radiation scattering
on the
particle and the
radiation absorption
by the particle. Together these processes
constitute
the radiation extinction
(the irradiance after interaction with the
particle is attenuated by the processes of scattering and absorption along the
incident beam direction
r
0
). Let the absorbed energy be equal to
E
a
,scattered
in all directions energy be equal to
E
s
, and the total attenuated energy be
equal to
E
e
=
E
a
+
E
s
. If the particle interacted with radiation according
to geometric optics laws and was a non-transparent one (i. e. attenuated all
incoming radiation), attenuated energy would correspond to energy incoming
to the projection of the particle on the plane perpendicular to the direction
of incoming radiation
r
0
. Otherwise, this projection is called the
cross-section
oftheparticlebyplane
and its area is simply called a
cross-section
.Measuring
attenuated energy
E
a
per wavelength and time intervals [
λ
λ
λ
], [
t
,
t
+
dt
]
according to the irradiance definition (1.3) we could find the extinction cross-
section as
dE
e
,
+
d
|
λ
dt
).
However, owing to the wave quantum nature of light its interaction with the
substance does not submit to the laws of geometric optics. Nevertheless, it is
very convenient to introduce the relation
dE
e
(
F
0
d
|
λ
dt
)thathasthedimension
and the meaning of the area, implying the equivalence of the energy of the real
interaction and the energy of the interaction with a nontransparent particle
possessing the cross-section equal to
dE
e
(
F
0
d
|
λ
dt
) in accordance with the laws
of geometric optics. Besides, it is also convenient to consider such a cross-
section separately for the different interaction processes. Thus, according to
the definition, the ratioof absorption energy
dE
a
,measuredwithin the intervals
[
(
F
0
d
λ
λ
λ
], [
t
,
t
+
dt
], to the incident radiation flux
F
0
is called an
absorption
cross-section
C
a
.Theratioofscatteringenergy
dE
s
to the incident radiation flux
is called
a scattering cross-section
C
s
and the ratio of total attenuated energy
dE
s
to the incident radiation flux is called
an extinction cross-section
C
e
:
,
+
d
dE
a
F
0
d
dE
s
F
0
d
dE
e
F
0
d
=
=
=
dt
=
C
a
,
C
s
,
C
e
C
a
+
C
s
.
(1.12)
λ
λ
λ
dt
dt
Fig. 1.4.
Definition of the cross-section of the interaction






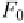
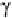










Search WWH ::

Custom Search