Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
X
2
r
x
t
r
x
t+
∆
t
X
1
X
3
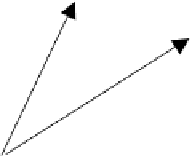
FIGURE 3.3
Trajectory of an elementary portion of fluid showing consecutive locations apart
in time of
∆
t
.
Considering a fluid as a continuum system, an elementary volume of fluid is a
portion of fluid so small that its properties (including velocity) can be considered
as uniform, but it is much bigger than the size of a molecule in laminar flow and
than an eddy in turbulent flow. In the case of a numerical model, an elementary
volume is the volume included inside a grid cell. As a consequence, diffusivity
increases with grid size in numerical models.
3.2.2
A
F
DVECTIVE
LUX
The advective flux accounts for the amount of a property transported per unit of
time due to fluid velocity across a surface perpendicular to the motion. Its dimensions
are [
BT
−
1
] and can be expressed as
†
B
V
V
t
Φ
adv
=
(3.2)
has the dimensions of a specific quantity
(amount per unit of volume) and is called the concentration. The ratio between the
volume and the time [
where
V
is the volume. The quantity
β
=
B
/
V
L
3
T
−
1
] is the flow rate that can be calculated as the product
†
[
B
] means “dimensions of
B
”;
T
means time.


























Search WWH ::

Custom Search