Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
800000
Mugil spp.
700000
R
2
= 0.72
600000
Opening of Marchamalo
artificial channel
500000
Enlargement of EI Estacio
artificial channel
400000
300000
Changes in
trophic status
200000
100000
0
140000
Sparus auratus
R
2
= 0.35
120000
100000
80000
60000
40000
20000
0
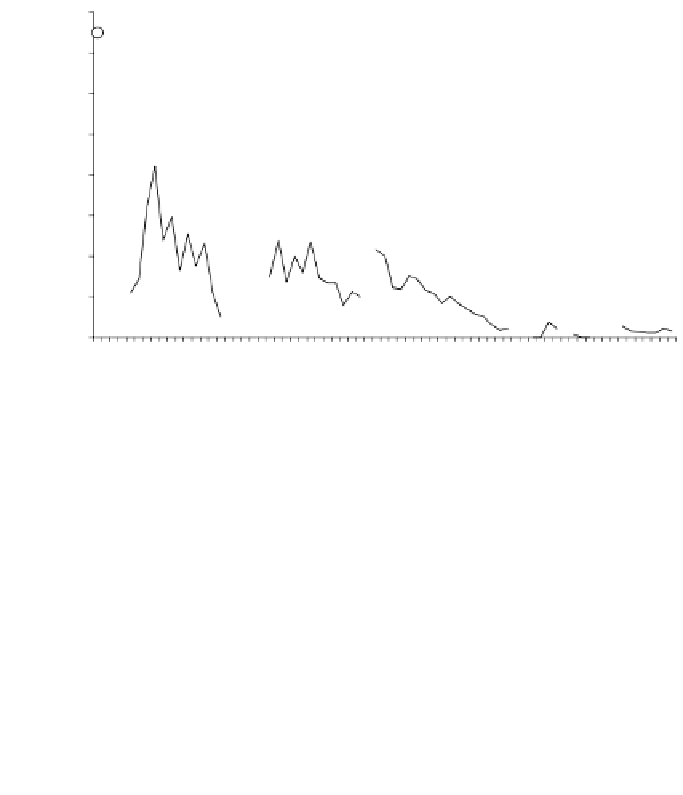
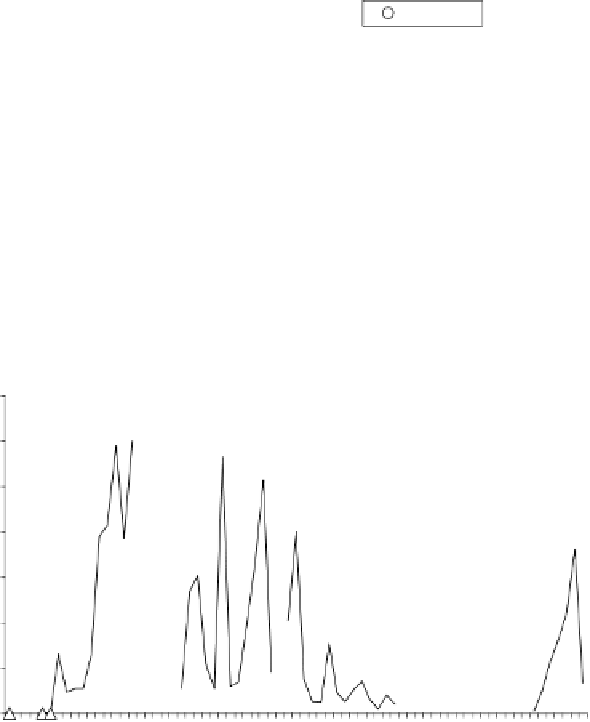
FIGURE 9.3.12
Evolution of catches of
Mugil
spp. and
Sparus auratus
in the Mar Menor
lagoon. Fisheries are artisanal and the fishing effort can be considered relatively constant over
time.
Physical, chemical, and biological data recorded for many different Mar Menor
programs over the years show some deviation from the rather classical pattern of
the eutrophication process. As mentioned above, intensive urban development for
tourism purposes started in the early 1970s, especially on La Manga. By that time,
the El Estacio Channel had opened and the largest yachting harbor in the lagoon
had been built. Simultaneously, summer residential areas were also built on the
lagoon's western coastline. Wastewater treatment plants were installed in the
main villages by the mid-1980s, but sewage overflow in many residential areas
was, and still continues to be, filtered into the lagoon after primary treatment.
Urban sewage is usually the main source of phosphorus in many Mediterranean








































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search