Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
River
stream
Open bay
Fjord
Lagoon
3
1
2
Choked type lagoon
Leaky type lagoon
Restricted type lagoon
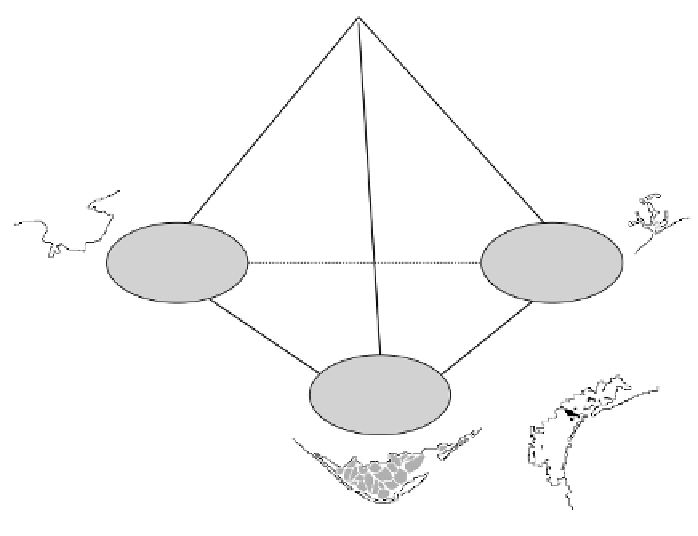
FIGURE 6.7.
Hydromorphometric tetrahedron presents the concept of pure types of coastal
water bodies and provides conventional coordinate systems and spaces where each point
corresponds to a water pool with “mixed” properties. Examples that illustrate the main shape
types of coastal lagoons
2,3
are (1) Darss-Zinst Bodden Chain Lagoon, Germany; (2) Ria
Formosa Lagoon, Portugal; and (3) Venice Lagoon, Italy.
shapes of lagoons
2
are presented (Figure 6.7) and may be considered as qualitative
features of these types, although, strictly speaking, the shape does not greatly influ-
ence lagoon hydrology.
A quantitative approach, based on some typical morphometric parameters,
may provide a deeper understanding of the physical processes at work in the
lagoon and highlight spatial scales of interest for the numerical model. For
example, a lagoon can be considered an idealized rectangular basin (
Figure 6.8)
with a cross-shore length
a,
an along-shore length
b
, a volume
V
, and an average
depth
H
. If the lagoon is round, it can still be considered as square, with equal
sides
a
and
b
. The lagoon entrance has a width
d
, a length
l
, and an average
depth
h
(Figure 6.8A,B).
This first-order approximation will yield the important spatial scales as well as
some insight into the physical processes to be modeled. The length scales obtained
will, in some cases, be comparable to those obtained by more elaborate methods that
use the real topography of the lagoon. This morphometric approach is recommended






















Search WWH ::

Custom Search