Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
There are many external sources of phosphorus for coastal ecosystems. Domestic
wastewater discharges may often contain large quantities of phosphorus because
many commercial cleaning products contain phosphorus. There are also industrial
sources of phosphorus, such as wastewater discharge from boiler water treatment
operations. Phosphates applied as fertilizers to agricultural or residential cultivated
land are also transported into surface waters with surface run-off. Internal sources
of phosphorus include benthic and pelagic regeneration.
Phosphorus in water can be classified into particulate and dissolved forms. Par-
ticulate phosphorus
includes phosphorus in organisms in/sorbed to dead organic
matter and in/sorbed to mineral phases of rock and soil. Dissolved phosphorus is
composed of orthophosphate (PO
4
−3
) polyphosphates (often originating from syn-
thetic detergents), organic colloids, and phosphorus combined with adsorptive col-
loids and low-molecular-weight phosphate esters. Orthophosphate is the most signif-
icant form of phosphorus available for phytoplankton growth. Orthophosphate ions
include phosphoric acid (H
3
PO
4
), its dissociation products (H
2
PO
4
−
, HPO
4
2−
, PO
4
3−
),
and the ion pairs and complexes of these products with other constituents in seawater.
The phosphorus atom has an oxidation state of
5 in orthophosphates.
7
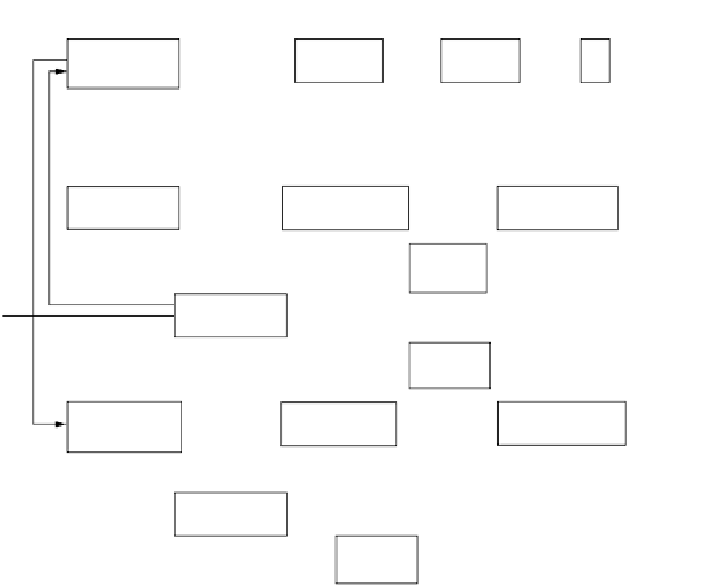
General phosphorus transformation mechanisms are illustrated in Figure 4.3. As
seen from this figure, phosphorus can undergo various reactions, depending upon
+
death and excretion
Nonliving
Particulate Organic
Phosphorus
Phytoplankton
Zooplankton
Fish
grazing
death
predation
desorption
mineralization
Dissolved Inorganic
Phosphorus (PO
4
Dissolved Organic
Phosphorus
Particulate Inorganic
Phosphorus
3
−
)
adsorption
Insoluble
Phosphorus
Compounds
death
precipitation
WATER
SEDIMENT
Rooted Aquatic
Plants
Insoluble
Phosphorus
Compounds
desorption
Nonliving
Particulate Organic
Phosphorus
decomposition
Dissolved Inorganic
Phosphorus
Particulate Inorganic
Phosphorus
adsorption
Dissolved Organic
Phosphorus
Phosphorus
Complexes
(Fe, Mn)
FIGURE 4.3
Phosphorus cycle.







































Search WWH ::

Custom Search