Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Drainage System (HRGC Green No. 2)
10
8
6
4
2
0
0
5
10
15
20
25
Easting, m
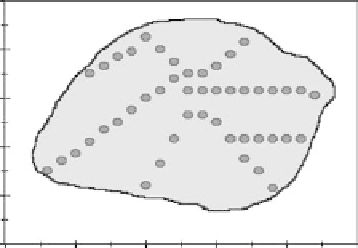
fIGURe 27.6
Map of Hickory Ridge golf green.
m
0.0
1.00
2.00
3.00
8.00
8.00
4.00
4.00
0.0
m/m
0.0
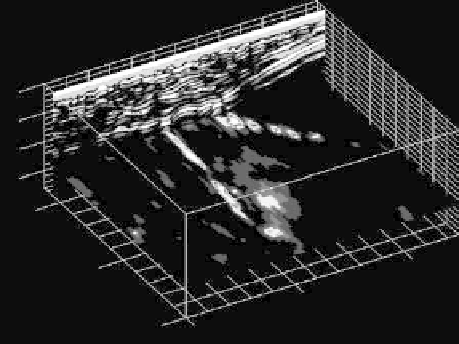
fIGURe 27.7
The three-dimensional image of the main and lateral drainage lines.
It is suggested that a GPS with high accuracy could be used for geo-referencing each location in the
process of scanning the green.
27.4 ConClUSIon
The golf green has the perfect condition for the use of GPR to detect underground features. Because
of its uniform profile, the response of the electrical permittivity of the soil profile is very consistent.
As the electromagnetic wave is transmitted, the velocity of the signal stays unchanged until it detects
the layer of gravel or a drain tile. The distinct changes in underground features provide definite
reflection. Much of the wave traveling below the clay and gravel interface tends to be scattered, so
this interface can be easily identified.
Using the GPR for locating and mapping drain tiles beneath golf greens can be very effective.
The noninvasive technology not only can provide accurate and quick answers to superintendents
who need to locate drain tiles, it can also detect rooting depth in golf greens. However, in the
process of measurement, flagging the green was rather time consuming. It is suggested that a high-
accuracy GPS could be used for geo-referencing the measuring of the boundary of the green and
scanning location.