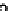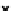Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
•
Veris 3100 (Veris Technologies, USA)
: The Veris 3100 is a GCR-based instrument working
at two depths. The rolling electrodes (smooth coulters) are arranged in a line with distances
of about 24 and 72 cm.
ARP-03 (Geocarta SA, France)
•
: The ARP-03 is a GCR instrument working at three depths.
Rolling electrodes (coulters with spikes) are arranged in a trapezoid pattern. Current elec-
trodes have a spacing of 1 m; potential electrodes have spacings of 0.5, 1, and 2 m (Dabas,
2002). Frequency is about 225 Hz; voltage can be varied between 0 and 200 V depending
on contact resistance conditions of a site (Geocarta SA, personal communications).
Earth Resistivity Meter 14.01 (Eijkelkamp, The Netherlands)
•
: The Earth Resistivity Meter
(ERM) is a GCR instrument for borehole measurements (direct push method). Four elec-
trodes in the sensor tip are arranged in a Wenner array. They sense approximately 80 cm³
of soil volume. Maximum depth of investigation is 1 m with a vertical resolution of about
5 cm. The probe has to be operated manually.
The GeoTom, the EM38, the EM38-MK2, and the ERM measurements were geo-referenced
by a measurement tape. Readings of all the other instruments were geo-referenced by differential
Global Positioning System (DGPS). Because of limited availability of the instruments and restric-
tions due to soil conditions, measurements were not always possible at the same time and at the
same site with all instruments.
22.2.3 d
a t a
a
n a l y s i s
We compared all surface methods with the raw data of the GeoTom. To avoid problems due to
nonlinearity, outliers, and deviations from normal distribution, we chose Kendall's tau (τ) rank cor-
relation coefficient to express similarities between the measurements. The τ values generally tend
to be lower when compared with Pearson's r correlation coefficient. Levels of significance are not
reported because all correlations were significant (
p
< 0.05 in all cases). Although readings were
not exactly colocated, we calculated τ for pairs of points within a specific distance (lag). To cor-
rect GPS errors and offsets, positions are shifted along the transects until τ is maximum. For GPS
geo-referenced measurements, lag width was set to 2 m and the shift increment to 0.5 m. For tape
measurements, the lag width was set to 1 m and the shift increment was 0.2 m.
Inversion is used to visualize the transects to compare the GeoTom with the borehole method
and to quantify spatial variability. Inversion is a
procedure that tries to estimate ER
a
for distinct,
nonoverlapping layers, excluding the influences
of the soil volumes that are on top. Calculations
were made with RES2DINV (Geotomo soft-
ware, Malaysia).
Kassow
Bornim
Golzow
1000
100
22.3 ReSUltS
Comparison of the ERM borehole instrument
with the inverted GeoTom data is shown in
Figure 22.2. The correlations for each single
test site were 0.559 at Bornim, 0.709 at Golzow,
and 0.896 at Kassow. No measurements with the
ERM were made at Beckum. The τ correlation
over all fields was 0.703 (Pearson's r is 0.871 for
log-log transformed values). This comparison
confirms the reliability of the GeoTom surface
readings.
10
10
100
1000
ERM (Ω m)
fIGURe 22.2
Log-log scatterplot of inverted sur-
face measurements by the GeoTom versus borehole
readings by the Earth Resistivity Meter (ERM).