Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
(b)
(c)
Soil drainage classes
WD
MWD
SWPD/PD
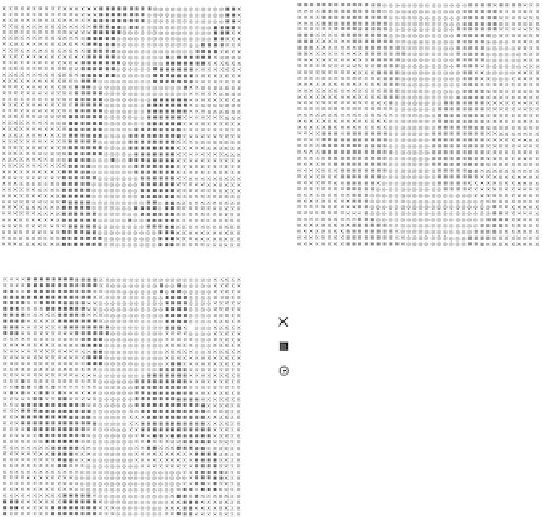
fIGURe 17.2
Drainage maps obtained from (a) discriminant analysis with deep electrical conductivity (EC) and
distance to drainageway, (b) indicator kriging based on the measured drainage classes , and (c) indicator cokriging
based on the measured drainage classes with slope and distance to drainageway as secondary variable.
discriminant analysis is not. That is, the maps created based on the discriminant analysis ignore the
actual data in sampled locations. Hence, indicator kriging and cokriging are preferable compared with
discriminant analysis for mapping purposes. Drainage maps obtained from (1) discriminant analysis
with deep EC and distance to drainageway, (2) indicator kriging, and (3) indicator cokriging with
slope and distance to drainageway are shown in Figure 17.2a through Figure 17.2c, respectively.
17.4 ConClUSIonS
Discriminant analysis identified terrain slope, deep (0 to 90 cm) EC measurements, and distance to
drainageway as the most useful secondary variables for predicting soil drainage classes. The com-
bination of discriminant analysis and geostatistics seems to be the most advantageous approach to
drainage class mapping. In this approach, the data are first analyzed with discriminant analysis, and
a limited number of variables with significant effect on the drainage classes are selected among all
the available topographical and soil variables. Then, the significant variables are used in the cokrig-
ing for the most accurate mapping of soil drainage classes.
RefeRenCeS
Bell, J.C., Cunningham, R.L., and Havens, M.W., Calibration and validation of a soil-landscape model for
predicting soil drainage class,
Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J.
, 56, 1860, 1992.
Bell, J.C., Cunningham, R.L., and Havens, M.W., Soil drainage probability mapping using a soil-landscape
model,
Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J.
, 58, 464, 1994.
Deutsch, C.V. and Journel, A.G.,
Geostatistical Software Library and User's Guide
, Oxford University Press,
New York, 1998.
Doolittle, J.A., Sudduth, K.A., Kitchen, N.R., and Indorant, S.J., Estimating depths to claypans using electro-
magnetic induction methods,
J. Soil Water Conserv.
, 49, 572, 1994.
Environmental Systems Research Institute, Inc.,
ArcView Spatial Analyst
, ESRI, Redlands, CA, 1996.