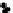Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
8
(a)
(b)
(c)
7
6
5
4
3
02468
10
12
14
16
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
20
30
40
50
60
EC
e
(dS/m)
Leaching Fraction
% Clay
8
(d)
(e)
(f)
7
6
5
4
3
7.0
7.2
7.4
7.6
7.8
8.0
8.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
1.4
1.5
1.6
1.7
Bulk Density (g/cm
3
)
pH
Gravimetric Water Content (g/g)
fIGURe 16.2
Scatter plots of soil properties and cotton yield: (a) electrical conductivity of the saturation
extract (EC
e
, dS m
−1
), (b) leaching fraction, (c) percentage clay, (d) pH, (e) gravimetric water content, and (f)
bulk density (Mg m
−3
). (Taken from Corwin, D.L., Lesch, S.M., Shouse, P.J., Soppe, R., Ayars, J.E.,
Agron. J.
,
95, 352-364, 2003. With permission.)
A scatter plot of EC
e
and yield indicates a quadratic relationship where yield increases and then
decreases (Figure 16.2a). The scatter plot of LF and yield shows a negative, curvilinear relationship
(Figure 16.2b). Yield shows a minimal response to LF below 0.4 and falls off rapidly for LF > 0.4.
Clay percentage, pH, θ
g
, and ρ
b
appear to be linearly related to yield to various degrees (Figure 16.2c
through Figure 16.2f, respectively). Even though there was clearly no correlation between yield and
pH (r = −0.01; see Figure 16.2d), pH became significant in the presence of the other variables, which
became apparent in both the preliminary MLR analysis and in the final yield response model. Based
on the exploratory statistical analysis, it became evident that the general form of the cotton yield
response model was
Y
= β
0
+ β
1
(EC
e
) + β
2
(EC
e
)
2
+ β
3
(LF)
2
+ β
4
(pH) + β
5
(% clay) + β
6
(θ
g
) + β
7
(ρ
b
) + ε
(16.1)
where, based on the scatter plots of Figure 16.2, the relationships between cotton yield (
Y
) and pH,
percentage clay, θ
g
, and ρ
b
are assumed linear; the relationship between yield and EC
e
is assumed to
be quadratic; the relationship between yield and LF is assumed to be curvilinear; β
0
, β
1
, β
2
, …, β
7
are the regression model parameters; and ε represents the random error component.
16.3.3 c
R o P
y
i e l d
R
e s P o n s e
M
o d e l
d
e v e l o P M e n t
Ordinary least squares regression based on Equation (16.1) resulted in the following crop yield
response model:
Y
= 20.90 + 0.38(EC
e
) - 0.02(EC
e
)2 - 3.51(LF)2 - 2.22(pH) + 9.27(θ
g
) + ε
(16.2)
where the nonsignificant
t
test for percentage clay and ρ
b
indicated that these soil properties did
not contribute to the yield predictions in a statistically meaningful manner and dropped out of the