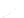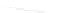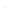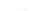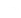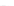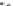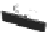Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Components
Input
Output
Management and Analytical Modules
Data Acquisition
Data Output
- Geodetic positioning
Analytical Modules
- Visual presentation
- Analog map output
- Reports
Management
- Remote sensing
- Field sampling
- Data conversion
- Data storage
- Data manipulation
- Modeling
- Data retrieval, expand
edit, and update
- Query
Analog Data Conversion
- Scan
- Digitize
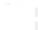
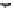
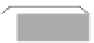
fIGURe 10.1
Components of a geographic information system (GIS).
and editing capabilities provide for a variety of software tools to store and maintain the digital
representation of the data sets. The database needs to be kept up-to-date, so editing tools are avail-
able to correct and update the data layers. Procedures to join maps and to perform edge matching
between adjacent map areas are also available.
Most GISs include a wide range of capabilities for analysis of geospatial data (geostatistics,
numerical methods, etc.). The output system is used to create high-quality maps, charts, and statisti-
cal summaries from analysis of the data layers residing in the spatial database. There are several
public domain and commercially available GIS software packages. These include ArcGIS, Geo-
Media, MapInfo, Idrisi, ERDAS, AUTOCAD MAP, MicroImages, and Manifold. Bolstad (2005)
provides a brief review of these software packages. There are several basic textbooks that provide
excellent descriptions of GIS concepts. These include works by Bolstad (2005), Bernhardsen (2002),
Bossler (2002), Chang (2002), Chrisman (2002), DeMers (2005), and Lo and Yeung (2002).
10.3 MAppInG ConCeptS
A GIS is composed of data layers that represent the different spatial properties of an area. Example
data layers that would be important for agricultural geophysics would include data layers of topog-
raphy, soil type, crop coverage, hydrologic features, land cover type, crop yield, and, of course, the
geophysical measurements. New spatial data layers can be derived from existing data layers. This
relationship can be defined as
NEW Layer = f (Existing Data Layers)
(10.1)
When using geospatial data models, the spatial properties of each data layer need to be considered.
This functionality can be expressed as the following:
F (P1, P2, …, Pn) x,y,z = f (P1)x,y,z + f (P2)x,y,z + … + f (Pn)x,y,z
(10.2)