Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
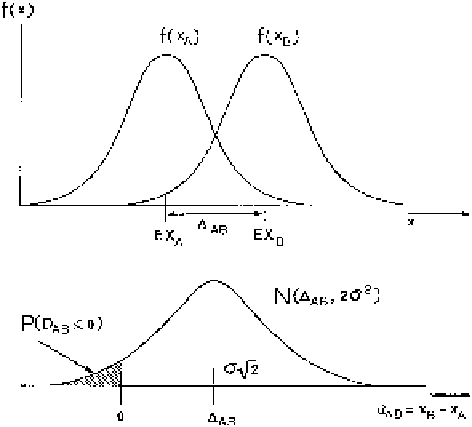
Fig. 9.4 Estimation of distance
ʔ
AB
between A and B from two-event inconsistencies frequency
p
(
D
AB
0). If
X
A
and
X
B
are random variables for location of events A and B
along the horizontal distance scale (
x
-axis), the random variable
D
AB
0)
¼
1
P
(
D
AB
<
>
x
B
is negative only
when order of A and B in section is reverse of order of the expected average locations
EX
A
and
EX
B
. The variance of
D
AB
is twice as large as the variance
¼
x
A
2
of the individual events A and B
σ
(Source: Agterberg
1990
, Fig. 6.5)
¼
¼
Ф
ʔ
ij
PD
ij
>
0
PD
ijk
>
0
where
P
denotes probability, and both
D
ij
and
D
ij
∙
k
¼
D
ik
D
jk
are normally dis-
tributed with expected values equal to
ʔ
ij
(
cf
. Agterberg
1990
, Equation 6.4).
In principle, this means that all other events (
k
) can be used to estimate the
interevent distance between any pair of events (
i
and
j
). In practice, other events
labeled
k
that are relatively far removed from the events labeled
i
and
j
cannot be
used because this would result in values of
1
or +
1
. RASC uses a variety of end
corrections to prevent this particular problem from significantly affecting the
interevent distance estimation.
The statistical model of scaling also can be clarified as follows. Suppose that,
along the RASC scale, all biostratigraphic events are normally distributed with
different mathematical expectations but with the same variance (
2
). Interevent
σ
2
, and
differences between interevent distances
D
ij
∙
k
are normally distributed with mean
ʔ
ij
and variance 3
distances
D
ij
then also are normally distributed with mean
ʔ
ij
but variance 2
·
σ
2
. Even if the original events do not have the same variance,
different
D
ij
∙
k
variances are not as different as original event variances because
these are being averaged. These considerations apply to an infinite statistical
population from which small samples are being drawn. For equations of small-
sample variances, see Agterberg (
1990
). Finally,
·
σ
it
is noted that
setting
D
ij
¼
Ф
1
(
p
ij
) implies
2
2. This arbitrary choice of variance controls the unit
for plotting events along the RASC interevent distance scale, which is relative.
σ
¼
Search WWH ::

Custom Search