Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
(b)
10
-3
×
0
0.4
-5
0.2
-10
0
-15
-20
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
-40
-20
0
dT/dr
dq/dr
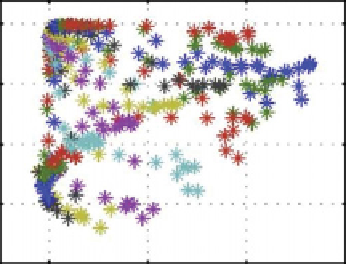
Figure 1.23.
Scatter plots of eddy fluxes of heat and potential vorticity against their respective zonal mean gradient fields in
numerical simulations by
Pérez
[2006]; and
Pérez et al.
[2010] of fully three-dimensional, time-dependent baroclinic waves flows
under moderately supercritical conditions (
= 0.15,
10
7
). Plots were obtained by plotting pointwise values of fluxes
and the respective radial gradient of the zonally averaged quantity across the whole meridional plane (outside boundary layers).
(a) Correlation of meridional heat flux against zonal mean temperature gradient. (b) Corresponding correlation for eddy fluxes
and zonal mean variations of QG potential vorticity. Adapted from
Pérez et al.
[2010]. Copyright 2010 with permission from
Elsevier.
T
= 1.30
×
relative) act directly down-gradient with respect to various
zonal mean fields in the simplest (right-cylindrical,
axisymmetric annular channel with flat horizontal bound-
aries) configuration of the annulus experiment.
They found that, contrary to the commonly held
assumption in many approaches that follow
Gent and
McWilliams
[1990] (hereafter referred to as GM90), the
horizontal eddy heat flux is only poorly correlated with the
lateral gradient of zonal mean temperature. Figure 1.23a
shows an example from Pé
rez e
t al.'s simulations in
wh
ich
the local eddy heat flux
(u
T
)
is plotted against
∂T/∂r
in an equilibrated baroclinic wave flow under moder-
ately super-critical conditions across the whole
(r
,
z)
plane
of the annulus.
Altho
ugh so
m
e structure is evident, the
dependence of
(u
T
)
on
∂T/∂r
is clearly a lot more
complicated than a simple, Fickian diffusive relationship
would suggest. This appeared to be typical of most fully
developed baroclinic wave simulations investigated by
Pérez et al.
[2010], with
anticorrelation is clearly evident, indicating that quasi-
geostrophic potential vorticity is diffused horizontally by
baroclinic eddies with respect to its zonal mean field to
quite a good approximation. This behavior was found to
be quite generic for almost all
case
s inves
t
igated, with
correlation coefficients between
u
q
and
∂q/∂r
ranging
from
0.9 for both equilibrated and transient
growing wave flows [
Pérez et al.
, 2010]. Similar behav-
ior was also found for relative vorticity, in fact with even
larger (negative) correlation coefficients than for potential
vorticity.
Given such a clear correlation between eddy fluxes and
mean gradients,
Pérez et al.
[2010] were able to deduce an
e
ffec
tive eddy
d
iffusivity
−
0.75 to
−
K
q
from a simple regression of
(u
q
)
against
∂q/∂r
in their model simulations. A straight-
forward linear regression led to the remarkable result that
K
q
varied by less than a factor of 2 across the whole range
of parameters investigated. Figure 1.24 shows the varia-
tion of the value of
0.2 in
most cases except either under marginally unstable con-
ditions or transiently during the initial growth of the
instability, when correlation coefficients as large as
|
correlation coefficients
|
K
q
obtained by
Pérez et al.
[2010] as a
function of boundary layer ratio
(also cf Figure 1.18),
indicating that, at least for these experiments,
P
K
q
was
10
−
2
cm
2
/s. The
−
0.7
found to vary slowly between 1-2
×
were found [
Pérez et al.
, 2010].
In contrast, fluxes of (potential or relative) vorticity
were found to act quite closely down-gradient in most
cases investigated. An example is shown in Figure 1.23b
for quasi-geostrophic potential vorticity, plotted in the
same way (and for the same case) as Figure 1.23a
over the whole annular domain. In this case a strong
largest values of
K
q
seemed to occur close to conditions
of marginal instability, with
K
q
gradually reducing toward
10
−
2
cm
2
/s for all
a roughly constant value
5.
Given these results,
Pérez et al.
[2010] further tried to
determine whether one or more previously proposed clo-
sures for
∼
P
were sufficient to represent the variations
found in their simulations based on an assumed form akin
K