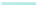Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
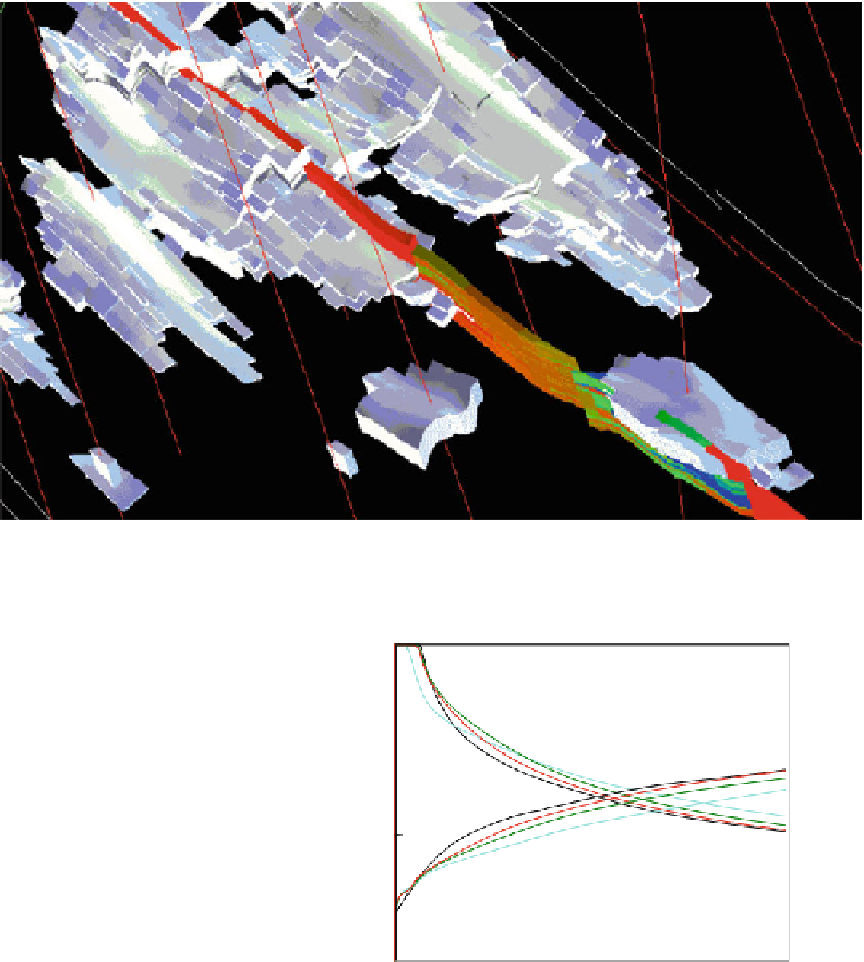
Fig. 4.30
Gas injection patterns in a thin-bedded tidal reservoir modelled using a multi-scale method and
incorporating the effects of faults in the reservoir simulation model (From a study by Brandsæter et al
2001b
)
Fig. 4.31
Effect of multi-
scale upscaling on
estimates of oil rate and
GOR for the gas injection
case study shown in
Fig.
4.30
(Redrawn from
Pickup et al.
2000
,
1.0
2500
Fine Grid
Coarse Grid (no upscaling)
Coarse Grid (one-step upscaling)
Coarse Grid (two-step upscaling)
2000
0.8
2000,
1500
#
0.6
Society of Petroleum
Engineers Inc., reproduced
with permission of SPE.
Further reproduction
prohibited without
permission)
1000
0.4
500
0.2
0
0
0
0.2
0.4
Volume Gas Injected (fraction of Free GIP)
cases. The modelling methods have achieved
sufficient speed and reliability for routine imple-
mentation (generally using steady-state methods
on near-orthogonal corner-point grid systems).
However, a number of challenges remain which
require further developments of methods and
modelling tools. In particular:
• Multi-scale modelling within a realistic struc-
tural geological grid is still a major challenge;
4.4
The Way Forward
4.4.1 Potential and Pitfalls
Multi-scale reservoir modelling has moved from
a conceptual phase, with method development on
idealised problems, into a practical phase, with
more routine implementation on real reservoir