Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
5. Have you run sensitivities to check important
assumptions?
6. Have you considered the effects of possible
un-detected flow barriers in the system?
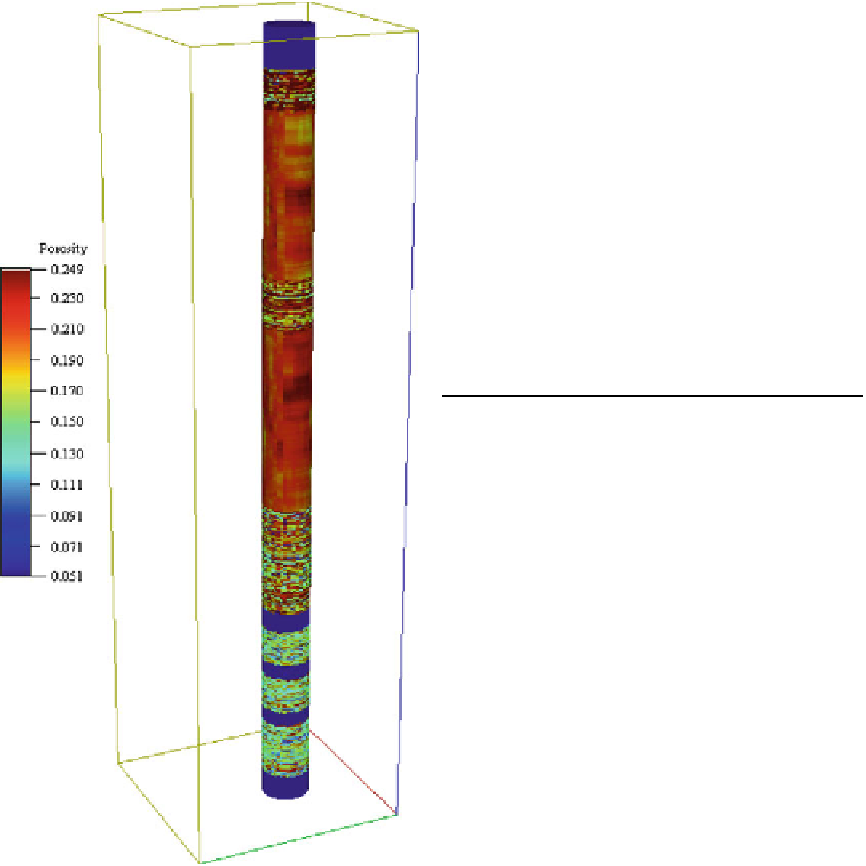
A final word about the future of property
modelling - if we are looking for fit-for-purpose
models for interpreting petrophysical well data,
then we are probably talking about high-
resolution near-wellbore models (Fig.
3.49
).
These models could be very detailed or could
be just a simple equation. Either way they need
to be focussed on the scale of rock property
variation - the subject of the next chapter.
References
Abbaszadeh M, Fujii H, Fujimoto F (1996) Permeability
prediction by hydraulic flow units - theory and
applications. SPE Form Eval 11(4):263-271
Begg SH, Carter RR, Dranfield P (1989) Assigning effec-
tive values to simulator gridblock parameters for het-
erogeneous reservoirs. SPE Reserv Eng 1989:455-463
Berg RR, DeMis WD, Mitsdarffer AR (1994) Hydrody-
namic effects on Mission Canyon (Mississippian) oil
accumulations, Billings Nose area, North Dakota.
AAPG Bull 78(4):501-518
Bierkins MFP (1996) Modeling hydraulic conductivity of
a complex confining layer at various spatial scales.
Water Resour Res 32(8):2369-2382
Bourbie T, Zinszner B (1985) Hydraulic and acoustic
properties as a function of porosity in Fontainebleau
sandstone. J Geophys Res 90(B13):11524-11532
Box GEP, Cox DR (1964) An analysis of transformations.
J R Stat Soc Series B: 211-243, discussion 244-252
Brandsæter I, McIlroy D, Lia O, Ringrose PS (2005)
Reservoir modelling of the Lajas outcrop (Argentina)
to constrain tidal
Fig. 3.49
Near-wellbore porosity model (1 m
2
reservoirs of
the Haltenbanken
10 m)
(Norway). Petrol Geosci 11:37-46
Bryant S, Blunt MJ (1992) Prediction of relative permeabil-
ity in simple porous media. Phys Rev A 46:2004-2011
Buland A, Kolbjornsen O, Omre H (2003) Rapid spatially
coupled AVO inversion in the fourier domain. Geo-
physics 68(1):824-836
Cardwell WT, Parsons RL (1945) Average permeabilities
of heterogeneous oil sands. Trans Am Inst Mining Met
Pet Eng 160:34-42
Corbett PWM, Jensen JL (1992) Estimating the mean
permeability: how many measurements do you need?
First Break 10:89-94
Corbett PWM, Ringrose PS, Jensen JL, Sorbie KS (1992)
Laminated clastic reservoirs: the interplay of capillary
pressure and sedimentary architecture. SPE paper
24699, presented at the SPE annual technical confer-
ence, Washington, DC
A consistent method for handling net-to-
gross (N/G) and cut-off values?
2. Is your petrophysical data representative of
the rock unit (sampling problems, tails of
distributions), and if not how will you address
that uncertainty?
3. Have you used appropriate averaging and/or
upscaling methods?
4. Is the model output consistent with data
input? Compare the statistics of input and
output distributions. The variance may be as
important as the mean.