Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Well data:
Treated as
continuous curve
Property Model:
Aims to represent all
reservoir properties
(sand, shale, cements)
Cut-offs
“Net reservoir” is defined after
geomodelling and upscaling
0.15
Modelled
non-reservoir
component
0.10
Classify rock
types, model and
upscale properties
0.05
0.00
0.01
0.1
1
10
100
1000
Permeability (md)
Fig. 3.33
Illustration of the total property modelling
approach (Redrawn from Ringrose
2008
,
#
2008, Society
of Petroleum Engineers Inc., reproduced with permission of
SPE. Further reproduction prohibited without permission)
Not measured due to
core damage, etc.
0.08
Measured
populations
0.06
Lower than
0.01md
0.04
> 10D due to
cracks/fractures
0.02
0.00
Permeability (md)
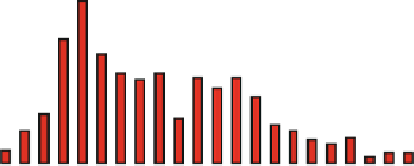
Fig. 3.34
Probe permeability dataset (5 mm-spaced
sampling for a 3 m reservoir interval) where
permeabilities between 0.01 mD and 10 Darcy have
been measured, and where the “lower-than measurable”
population has been identified (Redrawn from Ringrose
2008
,
#
2008, Society of Petroleum Engineers Inc.,
reproduced with permission of SPE. Further reproduction
prohibited without permission)
An important prerequisite for this approach is
that the petrophysical data must have been han-
dled appropriately. Net sand concepts are often
embedded in petrophysical logging procedures -
partly by dint of habit but also because shaly and
cemented rock properties are more difficult to
measure. Therefore, a major challenge for the
total property modelling approach is that prop-
erty estimation in poor reservoir quality units is
difficult or imprecise. However, if it is under-
stood that very low porosity and permeability
rock elements will be eventually discounted, it
is appropriate to assign a
reasonable guess
to the
low-quality reservoir units. This is illustrated by
the dataset from a very heterogeneous reservoir
unit shown in Fig.
3.34
.
Numerical upscaling is generally required
when applying the TPM approach (with the N/G
approach simple averaging is often assumed).
Valid application of numerical upscaling
methods requires that a number of criteria are
met - related to flow boundary conditions and
the statistical validity of the upscaled volume
(discussed in Chap.
4
). The Total Property