Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
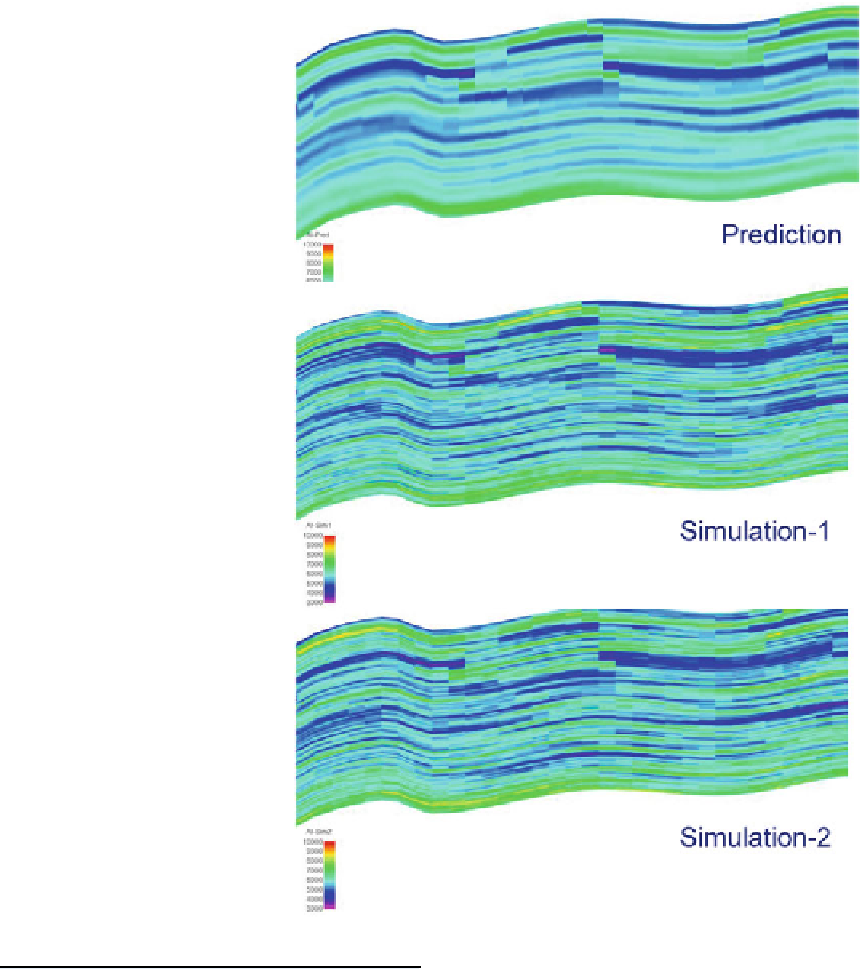
Fig. 3.27
Comparison of
AI predicted from seismic
inversion with two
stochastic simulations
integrating both the seismic
and the fine-scale well data
(From Nair et al.
2012
)
(Redrawn from Nair et al.
2012
,
#
EAGE reproduced
with kind permission of
EAGE Publications B.V.,
The Netherlands)
modelling work flow and discuss an alternative
approach termed total property modelling.
In the simplest case, a clastic reservoir can be
divided into a sand and shale components:
3.5
Use of Cut-Offs
and N/G Ratios
3.5.1 Introduction
N=G
¼
Sand volume fraction=Gross rock volume GRV
ð
Þ
The concept of the net-to-gross ratio (N/G) is
widespread in the oil business and consequently
reservoir modelling. Unfortunately, the concept
is applied in widely differing ways and poor use
of the concept can lead to serious errors. In this
section, we consider appropriate ways to handle
N/G in the context of a typical
In most cases rocks have variable sand content
and the sands themselves have variable reservoir
quality such that:
N
=
G
resevoir
6
¼
Sand volume fraction
=
GRV
:
The term 'net sand' is commonly defined with
respect to the gamma and porosity logs, as in the
reservoir