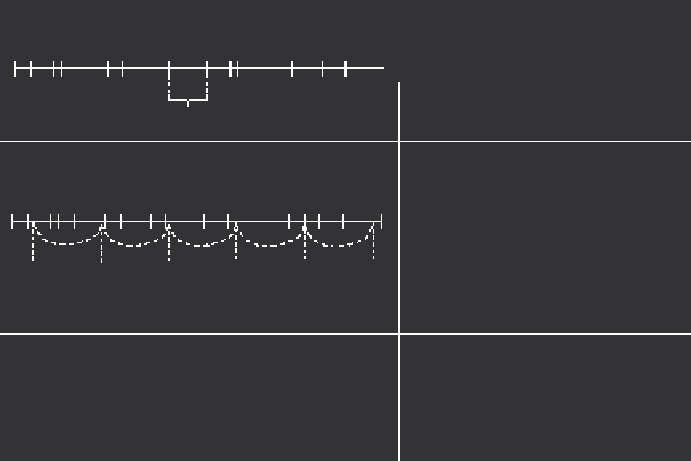
Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Step
1: Scale
x
to sum to
n
. If any π
> 1, set them = 1 and rescale
remaining to
n
- # (π > 1).
. . .
π
2
π
5
π
7
π
12
π
16
0
n
Segment length
proportional to
x
i
. . .
π
2
π
5
π
7
π
12
π
16
Step
2: Draw a systematic sample,
with random start and step
size 1, from line segment
0 to
n
.
0
n
m
m
+ 1
m
+ 2
m
+ 3
m
+ 4
m
+ 5
Step
3: Include units associated with
π's in the systematic sample.
S
= {
u
2
,
u
5
,
u
9
,
u
12
,
u
14
,
u
16
}
FIGURE 10.7
A heuristic pictorial representation of drawing a general random sample (GRS) of size
n
= 6
from a population of size
N
= 16.
is a simple random sample. If all elements in
x
are equal but the order of
units in the population is fixed, the resulting sample is a one-dimensional,
fixed-size systematic sample. This type of systematic sample is appropriate
when it is desirable to order units according to some auxiliary variable, such
as the distance from a geographic location, elevation, easting, or northing.
For example, it might be desirable to order stream segments by river mile
(distance from the mouth) to ensure that sample sites are located in all parts
of the river. If elements in
x
are not equal and the order of units is random-
ized, the resulting sample is a simple random sample with probability of
inclusion proportional to
x
. If elements in
x
are not equal but the order of
units is fixed, the resulting sample is a systematic sample with probability of
inclusion proportional to
x
.
10.4.2.3 Inclusion Probabilities for GRS
At analysis time, it is important to know or at least estimate the properties
of the sampling design under which data were collected. Principally, this
involves computing or estimating the design's first-order and second-order
inclusion probabilities. Third- and higher-order inclusion probabilities are
usually ignored. First-order and second-order inclusion probabilities are
important because they are used in the Horvitz-Thompson (Särndal et al
.
,
1992) and other estimation techniques.