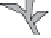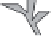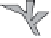Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Carbonate needles
released during breakdown
of calcareous green algae
(
Penicillus
,
Udotea
)
Inputs of calcareous
epibionts (coralline algae,
foraminifera, serpulids)
Breakdown of
Halimeda
Infaunal/epifaunal
sediment contributors
Longshore sediment
inputs/outputs
Terrigenous sediment
and anthropogenic
particulate inputs
Infaunal/epifaunal
skeletal inputs (molluscs,
echnioids)
Sediment reworking by
epifaunal detritivores
(Holothurians)
Lagoon sediments moved
seaward during storms
Onshore/offshore transport of
sediment during storms
Oolitic sand
formation
Winnowing of
bouyant grains
Sediment scouring
during storms
Sediment settling and
trapping within seagrass
beds
Fish grazing releases fine
carbonate sediment
Algal mats
stabilize
substrates
Breakdown of
calcareous
green algae
(
Halimeda
)
Deep sediment
bioturbation
by shrimps
Internal bioerosion
(sponges, bivalves,
worms)
Release of fragments
of calcareous encrusters
(coralline algae,
bryozoans, foraminifera)
Transport/reworking pathways
Production pathways
Breakdown of coral
framework and coral
rubble
Echinoid grazing produces
faecal carbonate pellets
Fig. 9.8
Schematic diagram illustrating the main sediment sources and transport pathways within coral-reef-related environments.