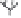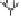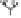Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
Reef
flat
Reef
crest
Back-reef/lagoon Reef front Fore-reef
Nutrients and
suspended
sediments
Physical
disturbance
Temperature
18 - 25-29 - 36
o
C
Wave base
Encrusting
Rigid branched
Photic
zone
Salinity
22 - 25-35 - 40
Mound/branched
Mound/massive
Sediment-dominated substrate
Framework-dominated substrate
Branched
1% surface
light illumination
Platy
Limit of
active coral
growth
Cool (nutrient-rich)
upwelling
(c)
(b)
Aragonite
Calcite
Coralline algae, molluscs,
foraminifera (coral and
calcareous green algae
present, but less
important)
Coralline algae,
mollusc and
bryozoan
dominated
sediments
Coral-algal reefs.
Ooid, coral and
calcareous green
algal dominated
sediments
30
25
20
15
10
5
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
4.5
4.0
3.5
0.5
0.0
3.0
0
o
10
o
30
o
40
o
50
o
60
o
0
o
10
o
20° 30
o
40
o
50
o
60
o
High-latitude coral
reefs with restricted
framework development
Latitude
Latitude
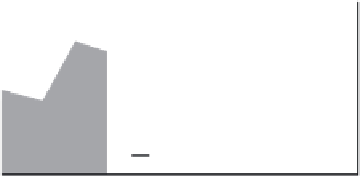
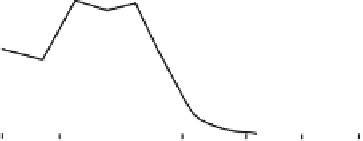
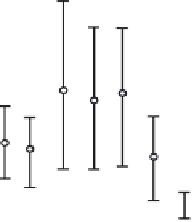
Fig. 9.3
(a) Environmental controls on the development of coral reef communities. (Adapted from James & Bourque 1994.) (b) Latitudinal changes in CaCO
3
accumulation rates
and (c) sea-surface temperature and aragonite saturation states. (Adapted from Buddemeier 1997; sediment types after Lees 1975.)