Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
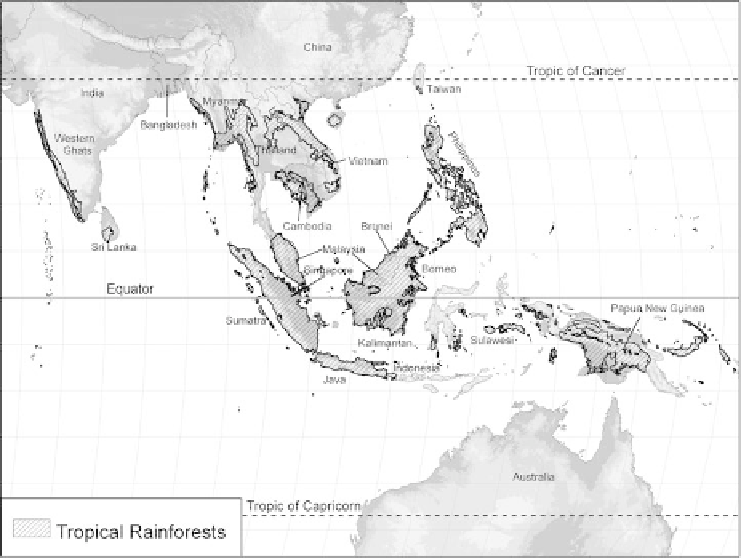
Indo-Asian Rainforest, and the Malesian Floristic Zone. The northern part of the
rainforest is located in tropical latitudes, along the west coast of India and Sri
Lanka, on continental Asia from Bangladesh and Myanmar (Burma) through
southern Thailand, the Laos People's Democratic Republic, Cambodia, and Viet-
nam, into southeast China and the Philippines. The heartland of the rainforest
lies on Malay Peninsula and the islands in the South China Sea, Malaysia, Bru-
nei, Sarawak, and the islands of Indonesia. Rainforest continues on the islands of
the Pacific in New Guinea and northeastern Australia and the islands of Melane-
sia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. The majority of the rainforest lies between 11
N
and 11
S latitude (see Figure 3.14). Monsoonal forests and savanna woodlands
border the rainforests within this region. In southern China, a belt of tropical
rainforest extends to 26
N, nourished by the warm wet winds from the Pacific
Ocean. The rainforest in India occurs in two distinct areas, in the northern state
of Assam close to the Myanmar border, and in a narrow strip in the Western
Ghats along the hills of the west coast on the country. Historically much larger in
extent, an estimated 0.61 million mi
2
(156 million ha) of these tropical forests
remain.
Figure 3.14 Location of tropical rainforests within the Asian-Pacific region.
(Map by
Bernd Kuennecke.)